Difference between revisions of "NU32"
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
[[Media:NU32_flyer.pdf|'''Flyer for the NU32 board and book (with Table of Contents).''']] |
[[Media:NU32_flyer.pdf|'''Flyer for the NU32 board and book (with Table of Contents).''']] |
||
[[Media:MicroSolutions-JanFeb-2016.pdf |
[[Media:MicroSolutions-JanFeb-2016.pdf|'''Read about the NU32 board, the book, and ME 333 Introduction to Mechatronics in Microchip's 'MicroSolutions' Newsletter, Jan/Feb 2016.''']] |
||
[http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/Market_Communication/MicroSolutions-JanFeb-2016.pdf#page=29 '''Read about the NU32 board, the book, and ME 333 Introduction to Mechatronics in Microchip's 'MicroSolutions' Newsletter, Jan/Feb 2016.'''] |
[http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/Market_Communication/MicroSolutions-JanFeb-2016.pdf#page=29 '''Read about the NU32 board, the book, and ME 333 Introduction to Mechatronics in Microchip's 'MicroSolutions' Newsletter, Jan/Feb 2016.'''] |
||
Revision as of 08:49, 10 June 2017
Home page of the NU32 PIC32 development board and the book "Embedded Computing and Mechatronics with the PIC32 Microcontroller" (Amazon, Elsevier), by Kevin M. Lynch, Nicholas Marchuk, and Matthew L. Elwin (Newnes/Elsevier, December 2015). The NU32 PIC32 development board accompanying the book can be purchased through Amazon.
Flyer for the NU32 board and book (with Table of Contents).
From the back cover
For the first time in a single reference, this book provides the beginner with a coherent and logical introduction to the hardware and software of the PIC32, bringing together key materials from the PIC32 Reference Manual, Data Sheets, XC32 C Compiler User's Guide, Assembler and Linker Guide, MIPS32 CPU manuals, and Harmony documentation. This book also teaches you to use the Microchip documentation, allowing better life-long learning of the PIC32. The philosophy is to get you started quickly, but to emphasize fundamentals and to eliminate "magic steps" that prevent a deep understanding of how the software you write connects to the hardware.
Applications focus on mechatronics: microprocessor-controlled electromechanical systems incorporating sensors and actuators. To support a learn-by-doing approach, you can follow the examples throughout the book using the sample code and your PIC32 development board. The exercises at the end of each chapter help you put your new skills to practice.
Features include:
- Extensive, freely downloadable sample code for the NU32 development board incorporating the PIC32MX795F512H microcontroller
- Free online instructional videos to support many of the chapters
Coverage includes:
- Getting up and running quickly with the PIC32
- An exploration of the hardware architecture of the PIC32 and differences between PIC32 families
- Fundamentals of embedded computing with the PIC32, including the build process, time- and memory-efficient programming, and interrupts
- A peripheral reference, with extensive sample code covering digital input and output, counter/timers, PWM, analog input, input capture, watchdog timer, and communication by the parallel master port, SPI, I2C, CAN, USB, and UART
- An introduction to the Microchip Harmony programming framework
- Essential topics in mechatronics, including interfacing sensors to the PIC32, digital signal processing, theory of operation and control of brushed DC motors, motor sizing and gearing, and other actuators such as stepper motors, RC servos, and brushless DC motors
- Appendices introducing the C programming language and background material on circuit analysis
This book is ideal for beginners, as a reference for professionals, or as a textbook for a college course on mechatronics.
Sample Chapters
The freely downloadable sample chapters include:
- the Table of Contents
- the Preface
- Chapter 1: Quickstart (getting up and running with the NU32 quickly)
- Chapter 2: Hardware (description of the PIC32 architecture, memory map, pins, peripherals, and special function registers, as well as the NU32 development board)
- Chapter 25: Brushed Permanent Magnet DC Motors (motor physics, speed-torque curve, and DC motor data sheets)
- Appendix A: A Crash Course in C
- Appendix B: Circuits Review
- Appendix C: Other PIC32 Models
Software
Links to software needed for the book are here: NU32 Software Downloads.
Videos
Videos to support several of the book chapters are posted here. Most of the videos were created using the Lightboard, an ingenious and easy-to-use device developed by Prof. Michael Peshkin at Northwestern University. Our gratitude goes to Prof. Peshkin.
The NU32
Purchasing
The NU32 board is available on Amazon. If Amazon does not ship to your country, please enter your email address here in this form so we can notify you when we have an alternative method to get you a board (we are working on it).
What's in the box:
- the NU32 development board (with the PIC32MX795F512H), with header pins already soldered for easy insertion into a solderless prototyping breadboard
- a solderless prototyping breadboard to insert the NU32 into
- a USB cable connecting your computer to the NU32, allowing you to program the PIC32 without any other programmer device, and allowing your PIC32 programs to communicate with your computer (e.g., MATLAB, a terminal emulator, Python, etc.) via a virtual serial port
- a 6V wall adapter that can be used to power the NU32
Description
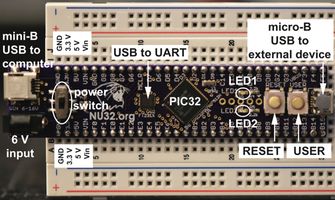
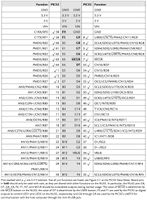
A photo of the NU32 development board is shown at the top of the page, and the pinout is given in the image to the right. The NU32 board provides easy breadboard access to most of the PIC32MX795F512H's 64 pins. The NU32 acts like a big 60-pin DIP (dual in-line package) chip and plugs into a standard prototyping breadboard.
Beyond simply breaking out the pins, the NU32 provides many features that make it easy to get started with the PIC32. For example, to power the PIC32, the NU32 provides a barrel jack that accepts a 1.35 mm inner diameter, 3.5 mm outer diameter center-positive power plug. The plug should provide 1 A at DC 6 V or more. The PIC32 requires a supply voltage VDD between 2.3 and 3.6 V, and the NU32 provides a 3.3 V voltage regulator providing a stable voltage source for the PIC32 and other electronics on board. Since it is often convenient to have a 5 V supply available, the NU32 also has a 5 V regulator. The power plug's raw input voltage Vin and ground, as well as the regulated 3.3 V and 5 V supplies, are made available to the user as shown in the photo at the top of the page and in the pinout. The power jack is directly connected to the Vin and GND pins so you could power the NU32 by putting Vin and GND on these pins directly and not connecting the power jack.
The 3.3 V regulator provides up to 800 mA and the 5 V regulator provides up to 1 A of current, provided the power supply can source that much current. In practice you should stay well under each of these limits. For example, you should not plan to draw more than 200 to 300 mA or so from the NU32. Even if you use a higher-current power supply, such as a battery, you should respect these limits, as the current has to flow through the relatively thin traces of the PCB. It is also not recommended to use high voltage supplies greater than 9 V or so, as the regulators will heat up.
Since motors tend to draw lots of current (even small motors may draw hundreds of milliamps up to several amps), do not try to power them from the NU32. Use a separate battery or power supply instead.
In addition to the voltage regulators, the NU32 provides an 8 MHz resonator as the source of the PIC32's 80 MHz clock signal. It also has a mini-B USB jack to connect your computer's USB port to a USB-to-UART FTDI chip that allows your PIC32 to use its UART to communicate with your computer.
A USB micro-B jack is provided to allow the PIC32 to speak USB to another external device, like a smartphone.
The NU32 board also has a power switch which connects or disconnect the input power supply to the voltage regulators, and two LEDs and two buttons (labeled USER and RESET) allowing very simple input and output. The two LEDs, LED1 and LED2, are connected at one end by a resistor to 3.3 V and the other end to digital outputs RF0 and RF1, respectively, so that they are off when those outputs are high and on when they are low. The USER and RESET buttons are attached to the digital input RD7 and MCLR pins, respectively, and both buttons are configured to give 0 V to these inputs when pressed and 3.3 V otherwise.
Because pins RG6 through RG9, RF0, RF1, and RD7 on the PIC32 are used for UART communication with the host computer, LEDs, and the USER button, other potential functions of these pins are not available if you would like to use the communication, LEDs, and USER button. In particular:
- UART6 is unavailable (conflicts with pins RG6 and RG9). Since UART3 is used for communication with the host computer, this leaves UART1, UART2, UART4, and UART5 for your programs.
- SPI2 is unavailable (conflicts with pins RG6 and RG7). This leaves SPI3 and SPI4.
- I2C4 is unavailable (conflicts with pins RG7 and RG8). This leaves I2C1, I2C3, and I2C5.
- The default CAN1 pins C1RX and C1TX cannot be used (they conflict with pins RF0 and RF1), but the configuration bit FCANIO in DEVCFG3 has been cleared to zero on the NU32, thereby setting CAN1 to use the alternate pins AC1RX (RF4) and AC1TX (RF5). Therefore no CAN module is lost.
- MII ethernet is unavailable (conflicts with pins RD7, RF0, and RF1). The PIC32 can implement ethernet communication using either the media-independent interface (MII) or the reduced media-independent interface (RMII), and RMII ethernet communication, which uses many fewer pins than MII, is still available on the NU32.
- Several change notification and digital I/O pins are unavailable, but many more remain.
In all, very little functionality is unavailable due to connections on the NU32, and advanced users can find ways to bypass even these limitations.
Design files
The NU32 was designed in EAGLE v7. PDFs, EAGLE files, gerber files, and BOM are provided here: NU32v7_designfiles_dec2015.zip
Bootloader
If for some reason you do not want to use the bootloader that comes pre-installed on the NU32, you can program the PIC32 using an external programming device like the PICkit 3, as shown in the image on the right. Simply use header pins in the PICkit 3 connector to lean against the plated holes on the NU32, as shown. Your software must set the configuration bits, and you will likely overwrite the pre-installed bootloader. You can also use an external programmer to install a new bootloader.
- The bootloader source code is included within the full book source code on the NU32 Software Download page.
- The current bootloader hex file is provided here: NU32bootloader_5_2.hex. The old version is here: NU32bootloader_5_0.hex.
If your board has bootloader version 5.0 there is no need to update, the changes were mainly to make the code compile with xc32 v1.40.
Other
- Powering the NU32 from your USB port (coming soon).
Forum
Have a question about the book or the NU32, or want to share a project? Post on the NU32 google forum.
Purchasing a Kit of Parts
A listing of parts used in the book with the NU32, and where to buy them, can be found on this page. The "kits" are broken into (1) the minimum recommended kit of electronics, (2) components for the brushed DC motor control project, (3) other useful components accompanying source code in the book, and (4) other parts used or referenced in the book.
An Inexpensive Portable Oscilloscope and Function Generator: the nScope
Several courses at Northwestern, including ME 333 Introduction to Mechatronics, use the nScope, a portable function generator and oscilloscope that plugs into a breadboard and uses your laptop for its display. You will find a device like this quite useful when completing some of the exercises in the book or when exploring the peripherals of the PIC32 further. Information on the nScope, including its specs and ordering information, can be found here.
Book Errata
Corrections to the book are provided here.
A Self-Study Course
The curriculum below is based on ME 333 Introduction to Mechatronics at Northwestern, taken by sophomores through graduate students. Resources include the book chapters (with exercises at the end), instructional videos, the sample code, and the NU32 development board and other equipment. The links below are to the YouTube playlists with videos accompanying book chapters. All videos can be found at this YouTube channel.
ME 333 is an 11-week course, and the chapters below are covered in the course. Other chapters are listed under "Extensions."
Preliminaries
- Appendix A: A Crash Course in C. (This can be skipped by those experienced in C programming.)
- Appendix B: Circuits Review. (This is primarily reference material.)
The PIC32 Microcontroller
- Chapter 1: Quickstart. (Mac, Linux, Windows)
- Chapter 2: Hardware.
- Chapter 3: Software.
- Chapter 4: Using Libraries.
- Chapter 5: Time and Space.
- Chapter 6: Interrupts.
- Chapter 7: Digital Input and Output.
- Chapter 8: Counter/Timers.
- Chapter 9: Output Compare.
- Chapter 10: Analog Input.
Mechatronics
- Chapter 21: Sensors.
- Chapter 23: PID Feedback Control.
- Chapter 24: Feedback Control of LED Brightness.
- Chapter 25: Brushed Permanent Magnet DC Motors.
- Chapter 26: Gearing and Motor Sizing.
- Chapter 27: DC Motor Control.
- Chapter 28: A Motor Control Project.
Extensions
Chapters 11-20 on other PIC32 peripherals and the Harmony software framework; Chapter 22 on Digital Signal Processing; and Chapter 29 on Other Actuators (solenoids, voice coil actuators, RC servo motors, stepper motors, and brushless motors).
Data Sheets
The PIC32
References relevant to the PIC32 hardware:
- Local copy of the PIC32MX5xx/6xx/7xx Family Data Sheet (Dec 2013) (this is all that is needed for the NU32, but see Microchip's site for up-to-date documentation)
- Local copy of the PIC32 Reference Manual (Dec 2013) (this concatenates many of the individual Reference Manual sections and is all that is needed for the NU32---and in fact is more than is needed since the PIC32MX795F512H does not support some of the features described---but see Microchip's site for up-to-date documentation)
Documentation relevant to PIC32 software, including the MPLAB X Integrated Development Environment, the Harmony software framework, and the XC32 C/C++ compiler, can be found on Microchip's website by following the previous links, or you can download some of the most relevant documentation below as of December 2015:
- MPLAB XC32 C/C++ Compiler User's Guide
- MPASM Assembler, MPLINK Object Linker, MPLIB Object Librarian User's Guide
- MPLAB XC32 Assembler, Linker, and Utilities User's Guide
- MPLAB X IDE User's Guide (the IDE is not used in the book, as we believe the command line approach taken in the book is more direct, faster, and less "magic," but that's a matter of taste!)
The PIC32MX795F512H uses the MIPS32 M4K processor core by Imagination Technologies. You can learn more about it from the references below or by visiting Imagination Technologies:
- MIPS32 M4K Processor Core Data Sheet
- MIPS32 M4K Processor Core Software User's Manual
- MIPS32 Instruction Set Quick Reference
- MIPS Architecture For Programmers Volume I-A: Introduction to the MIPS32 Architecture
- MIPS Architecture For Programmers Volume II-A: The MIPS32 Instruction Set Manual
Other Devices
These are data sheets of some of the other devices referenced in the book.
- Chapter 4
- Chapter 12
- Chapter 13
- Chapter 19
- Chapter 21
- Advanced Photonix PDV-P5002 photocell
- OPTEK Technology OP906 photodiode
- Fairchild Semiconductor QED123 LED
- OSRAM SFH 310 NPN phototransistor
- Kingbright WP7113SRC/DU red LED
- OPTEK Technology photointerrupter
- OPTEK Technology OPB742 reflective object sensor
- Contelec WAL305 potentiometer
- Avago Technologies AEAT-9000-1GSH1 absolute optical encoder
- Analog Devices AD2S90 resolver-to-digital converter chip
- Omega LD320 linear variable differential transformer
- Analog Devices AD698 universal LVDT signal conditioner chip
- Analog Devices ADXL362 three-axis accelerometer
- STMicroelectronics L3GD20H three-axis gyro
- STMicroelectronics ASM330LXH inertial measurement unit (IMU)
- Toshiba TCS20DPR digital Hall effect switch
- Avago Technologies AEAT-6600 angular magnetic encoder IC
- Sharp infrared distance sensor
- TDK B57164K103J negative temperature coefficient thermistor
- Analog Devices TMP37 temperature sensor
- Maxim Integrated MAX9918 current-sense amplifier
- Allegro ACS711 Hall-effect current sensor
- Chapter 27
- Chapter 29
- Fairchild Semiconductor TIP120 NPN transistor
- Fairchild Semiconductor 1N4001 diode
- H2W Technologies NCC-05-11-011-1PBS moving coil voice coil actuator
- Texas Instruments DRV8825 stepper motor controller IC
- Pittman ELCOM-SL-4443S013 brushless motor
- STMicroelectronics L6234 three phase brushless motor driver
About the Authors
Kevin Lynch received his BSE in Electrical Engineering from Princeton University and his PhD in Robotics from Carnegie Mellon University, and he is currently Professor and Chair of the Mechanical Engineering Department at Northwestern University. He has been teaching robotics and mechatronics at Northwestern for over 15 years, and he has been awarded Northwestern’s highest teaching awards. He publishes and lectures widely on his research in robotics. He is a Fellow of the IEEE.
Nick Marchuk is a Lecturer in Mechatronics and directs the Mechatronics Design Lab at Northwestern University. He teaches introductory and advanced courses in mechatronics and directs student projects in electromechanical design. He received his BS degree in Mechanical Engineering from Johns Hopkins University and his MS in Mechanical Engineering from Northwestern.
Matthew Elwin is currently a PhD candidate in Mechanical Engineering at Northwestern University, where he has served as a teaching assistant for its mechatronics course. He earned BA and BE degrees in engineering sciences from Dartmouth College in 2009 and his MS in Mechanical Engineering from Northwestern in 2013. His research is in swarm robotics.