Difference between revisions of "Data logging with an EEPROM"
Neil Tiwari (talk | contribs) (→Code) |
Neil Tiwari (talk | contribs) (→Code) |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
#include <18f4520.h> |
#include <18f4520.h> |
||
#fuses HS,NOLVP,NOWDT,NOPROTECT |
#fuses HS,NOLVP,NOWDT,NOPROTECT |
||
#use delay(clock=40000000) |
#use delay(clock=40000000) |
||
#use i2c(MASTER, FAST, SCL=PIN_C3, SDA=PIN_C4, FORCE_HW) // use hardware i2c controller |
#use i2c(MASTER, FAST, SCL=PIN_C3, SDA=PIN_C4, FORCE_HW) // use hardware i2c controller |
||
#use rs232(baud=9600, UART1) // Set up PIC UART on RC6 (tx) and RC7 (rx) |
#use rs232(baud=9600, UART1) // Set up PIC UART on RC6 (tx) and RC7 (rx) |
||
#define EEPROM_WR 0xA0 // Define initial EEPROM write address block (See EEPROM data sheet) |
#define EEPROM_WR 0xA0 // Define initial EEPROM write address block (See EEPROM data sheet) |
||
#define EEPROM_RD 0xA1 // Define initial EEPROM read address block (See EEPROM data sheet) |
#define EEPROM_RD 0xA1 // Define initial EEPROM read address block (See EEPROM data sheet) |
||
int button1, button2, data_rx = 48; // Initialize variables |
int button1, button2, data_rx = 48; // Initialize variables |
||
int16 i, temp, value, address = 0, data; |
int16 i, temp, value, address = 0, data; |
||
void seq_write(int16 address, int16 data)//Writing to the EEPROM function |
void seq_write(int16 address, int16 data)//Writing to the EEPROM function |
||
{ |
{ |
||
i2c_start(); |
i2c_start(); |
||
i2c_write(EEPROM_WR); |
i2c_write(EEPROM_WR); |
||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
i2c_stop(); |
i2c_stop(); |
||
delay_ms(5);//Delay time needed in order to allow EEPROM to write data from buffer to memory sector |
delay_ms(5);//Delay time needed in order to allow EEPROM to write data from buffer to memory sector |
||
} |
} |
||
int16 seq_read(int16 address)// Reading from the EEPROM function |
int16 seq_read(int16 address)// Reading from the EEPROM function |
||
{ |
{ |
||
i2c_start(); |
i2c_start(); |
||
i2c_write(EEPROM_WR); |
i2c_write(EEPROM_WR); |
||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
i2c_stop(); |
i2c_stop(); |
||
return(value); |
return(value); |
||
} |
} |
||
void main() //Main Function |
void main() //Main Function |
||
{ |
{ |
||
setup_adc_ports(AN0); //Setup Analog Inputs |
setup_adc_ports(AN0); //Setup Analog Inputs |
||
set_adc_channel(0); |
set_adc_channel(0); |
||
setup_adc(ADC_CLOCK_INTERNAL); |
setup_adc(ADC_CLOCK_INTERNAL); |
||
while (TRUE) |
while (TRUE) |
||
| Line 119: | Line 119: | ||
} |
} |
||
} |
} |
||
} |
} |
||
Revision as of 18:14, 11 February 2009
Original Assignment
Your task is to use the PIC to log data from an analog input on an EEPROM, and after the data collection is over, to send the data back from the EEPROM to a PC running matlab. Use an interrupt service routine to read an analog input and write the value to an external EEPROM using I2C. After reading in a fixed number of samples, perhaps 1,000 or 10,000, the program should send the data back to a matlab program via an RS-232 link. The logged data should then be plotted by matlab.
You should decrease the sample time until the ISR does not successfully complete. What is the fastest rate at which an analog input can be read and stored to the external EEPROM? Try this for an analog input configured for both 8-bit (1 byte of data stored on the EEPROM) and 10-bit (2 bytes of data stored on the EEPROM). How much data can you store on the EEPROM?
As an alternative, you can avoid the use of an ISR and simply read and store the data as fast as you can in a loop.
As a test input, use a triangle wave signal from the function generator between 1 and 4 V, and plot the data in matlab.
See Interfacing to External EEPROM, PIC RS232, and Serial communication with Matlab.
Overview
An external EEPROM is useful when trying to store data. In addition to an external EEPROM being capable of storing much more data than is available on the 18F4520 PIC, the data is stored even when power is removed and can then be collected at a later time. Storing large amounts of data over time is especially beneficial once communication can be made between the PIC and Matlab. Using the serial function in Matlab, the data can be obtained and then analyzed.
In this project, we used the PIC to log data from an analog input onto an EEPROM and then later sent the data back from the EEPROM to Matlab to plot. For our lab, we worked with a 24FC1025 EEPROM whose data sheet can be found here (http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/21941B.pdf). Additionally, we established serial port connection between the PIC microcontroller and Matlab using the RS232 (http://hades.mech.northwestern.edu/wiki/index.php/PIC_RS232).
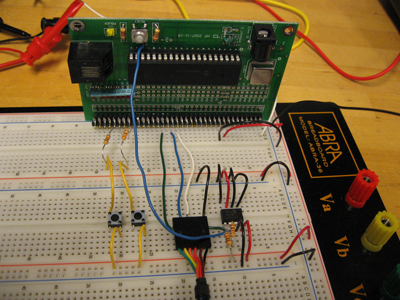
Circuit
(Images coming soon) To the right is a circuit diagram for interfacing a Microchip 24FC1025 EEPROM to the 18F4520 PIC. Below the diagram is an actual photo of the circuit layout.
[Pin descriptions necessary]
In order to connect our PIC to Matlab, we use a RS232. As mentioned here (http://hades.mech.northwestern.edu/wiki/index.php/PIC_RS232), we connect the black wire to ground, the orange wire to pin 26, RC7 and the yellow wire to pin 25, RC6.
Code
This project consists of two sets of code: code that is downloaded to the PIC to collect and store data to and send data from the EEPROM , and code that is used by Matlab to collect and plot the data. Within our code, we use a delay time is 5 msec since this is the time required to write the data to the EEPROM. We also collect 1000 data points which is the maximum number of points available. [Not completely confident in the previous statment.] The EEPROM is storing 1024K bits or 128K bytes.
[PIC CODE]
#include <18f4520.h> #fuses HS,NOLVP,NOWDT,NOPROTECT #use delay(clock=40000000) #use i2c(MASTER, FAST, SCL=PIN_C3, SDA=PIN_C4, FORCE_HW) // use hardware i2c controller #use rs232(baud=9600, UART1) // Set up PIC UART on RC6 (tx) and RC7 (rx) #define EEPROM_WR 0xA0 // Define initial EEPROM write address block (See EEPROM data sheet) #define EEPROM_RD 0xA1 // Define initial EEPROM read address block (See EEPROM data sheet)
int button1, button2, data_rx = 48; // Initialize variables int16 i, temp, value, address = 0, data;
void seq_write(int16 address, int16 data)//Writing to the EEPROM function
{
i2c_start();
i2c_write(EEPROM_WR);
i2c_write(address>>8);
i2c_write(address);
i2c_write(data);
i2c_stop();
delay_ms(5);//Delay time needed in order to allow EEPROM to write data from buffer to memory sector
}
int16 seq_read(int16 address)// Reading from the EEPROM function
{
i2c_start();
i2c_write(EEPROM_WR);
i2c_write(address>>8);
i2c_write(address);
i2c_start();
i2c_write(EEPROM_RD);
value = i2c_read(0);
i2c_stop();
return(value);
}
void main() //Main Function
{
setup_adc_ports(AN0); //Setup Analog Inputs
set_adc_channel(0);
setup_adc(ADC_CLOCK_INTERNAL);
while (TRUE)
{
button1 = input(PIN_D0); // Button one is pressed when the user wants to write to the EEPROM
button2 = input(PIN_D1); // Button two is pressed when the user wants to read from the EEPROM and send the data to Matlab
if (button1 == 1) {
output_high(PIN_D0);//LED is turned on to show that writing to the EEPROM has begun
address = 0x00;
for (i=0; i<1000; i++){
data = read_adc();//Read in data from analog input (In this case it was attached to a function generator)
//printf("Hello world. %Lu %Lu\r\n", i, data);
//data++;
seq_write(address, data); // Send data from analog input to write function
address++; // Increment up the address location on the EEPROM for the next time it writes something
}
output_low(PIN_D0); // LED is turned off to show that writing to the EEPROM is complete
}
if (button2 == 1) {
address = 0x00; // start at the first address location
while (data_rx == 48) {
output_high(PIN_D1);
if (kbhit()){
data_rx = fgetc();
temp = seq_read(address); //read data from adress location
printf("%lu \r",temp); // sends data to serial port
address++; // increment up the address so it can read from the next data sector
}
button1 = input(PIN_D0);
if (button1 == 1){
output_low(PIN_D1);
data_rx = 48; // 48 is the ASCII Code for integer '0'
delay_ms(500);
break;// Basically break from this loop if user presses the first button
}
}
data_rx = 48; // 48 is the ASCII Code for integer '0'
}
}
}
[Matlab Code]
%Construct serial port object
%deletes any serial port objects that exist in memory delete(instrfind) %Define serial COM Port s1 = serial('COM8'); %Open the com port fopen(s1);
set(s1,'Terminator','CR');
%Length of data points to be retrieved from EEPROM final = 1000;
%For loop for retrieving data from the EEPROM for ii = 1:final
if ii ~= final
%Send EEPROM "0" to signal that a data point should be sent
fprintf(s1,'%s','0')
%Get data point from eeprom
x(ii) = fscanf(s1,'%g');
else
%At the very last data point send EEPROM "1" to terminate the
%sending process
fprintf(s1,'%s','1')
% Get final data point from EEPROM
x(ii) = fscanf(s1,'%g');
end
end
%Close serial port fclose(s1); %Delete serial port object delete(s1); %Plot retrieved data plot(x)
Further Reading
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/EEPROM
http://hades.mech.northwestern.edu/wiki/index.php/Serial_communication_with_Matlab