Difference between revisions of "Driving a DC Motor using PWM"
From Mech
Jump to navigationJump to searchm |
|||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Note: this page describes one of two ways of doing PWM. This way uses two PWM signals inverse to each other. The other way uses one PWM signal and a DC level. See [[Pulse_width_modulation]] |
|||
Before doing this exercise, read about [[Brushed DC Motor Theory|Brushed DC Motors]] and [[Pulse Width Modulation|Driving Using Pulse Width Modulation]]. In this exercise you will use a function generator to create the pulse width modulation (PWM) signal that controls the motor. This simulates a signal that could be generated by a microcontroller. |
Before doing this exercise, read about [[Brushed DC Motor Theory|Brushed DC Motors]] and [[Pulse Width Modulation|Driving Using Pulse Width Modulation]]. In this exercise you will use a function generator to create the pulse width modulation (PWM) signal that controls the motor. This simulates a signal that could be generated by a microcontroller. |
||
Make sure your 7.2V battery pack is charged. The steps below assume you are using [http://www.hobbyengineering.com/H1209.html this gearmotor], which has a 224:1 gearhead and a stall torque of 50 oz-in at 5V, with a stall current of 600 mA. |
|||
Make sure your 7.2V battery pack is charged. |
|||
<ol> |
<ol> |
||
[[Image:PWM-low-duty-cycle-small2.jpg|right]] |
|||
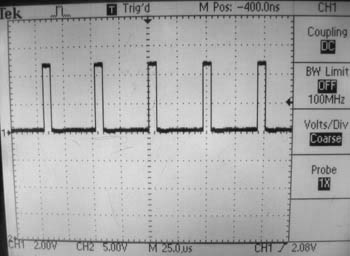
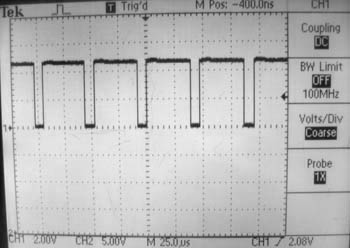
| ⚫ | <li> Use a function generator to create a |
||
| ⚫ | <li> Use a function generator to create a 5 kHz square wave between 0V (GND) and 5V. Verify that you have done this by looking at the signal on an oscilloscope. ('''Note:''' In the figures below, I used a 20 kHz square wave, an unnecessarily high switching frequency for this exercise.) To learn how to do this with the function generator and oscilloscopes in the Mechatronics Lab, read the manuals on the [[Tektronix CFG253 Function Generator]] and [[Tektronix TDS220 Oscilloscope]]. Looking at the oscilloscope signal, vary the duty cycle (the percentage of time the signal is "high" each cycle) of the signal using the symmetry knob, say from 20% to 80%. Your oscilloscope should look something like the figures below. |
||
<br clear=all> |
<br clear=all> |
||
[[Image:PWM-high-duty-cycle-small2.jpg|right]] |
|||
<li> Attach your battery pack to your breadboard. Use your [[media:LM7805.pdf|7805 1A 5V voltage regulator]] so that you have 5V and 7.2V (with respect to the ground pin of the voltage regulator) available for use. Verify using your multimeter or an oscilloscope. (In my case, I measured about 5.2V and 9.5V.) Make sure your function generator ground is connected to the ground pin of the voltage regulator. '''Note:''' Don't try to jam the 7805 leads into a protoboard, as they are too large. Solder 22 AWG solid wires to the leads instead. |
<li> Attach your battery pack to your breadboard. Use your [[media:LM7805.pdf|7805 1A 5V voltage regulator]] so that you have 5V and 7.2V (with respect to the ground pin of the voltage regulator) available for use. Verify using your multimeter or an oscilloscope. (In my case, I measured about 5.2V and 9.5V.) Make sure your function generator ground is connected to the ground pin of the voltage regulator. '''Note:''' Don't try to jam the 7805 leads into a protoboard, as they are too large. Solder 22 AWG solid wires to the leads instead. |
||
<br clear=all> |
|||
[[Image:PWM-signals-small2.jpg|right]] |
|||
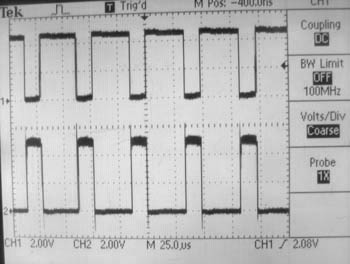
<li> Use a [[media:SN74HC04.pdf|74HC04 Hex Inverter/Buffer]] to get an inverted version of the function generator signal, in addition to the original signal. (Don't forget to power this chip!) Verify by looking at both the original signal and the inverted signal simultaneously on the oscilloscope. You should see something like below: |
<li> Use a [[media:SN74HC04.pdf|74HC04 Hex Inverter/Buffer]] to get an inverted version of the function generator signal, in addition to the original signal. (Don't forget to power this chip!) Verify by looking at both the original signal and the inverted signal simultaneously on the oscilloscope. You should see something like below: |
||
<br clear=all> |
<br clear=all> |
||
[[Image: |
[[Image:H-bridge-outs-small2.jpg|right]] |
||
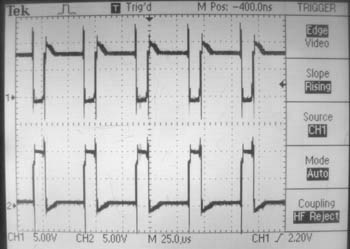
| ⚫ | <li> Send these two signals (original and inverted) to inputs 2 and 7 of an [[media:L293.pdf|L293B H-bridge]]. Make sure this H-bridge chip is correctly powered by attaching +5V to the Vss pin (the "logic" power supply) and the battery's +7.2V to the Vs pin (the motor power supply). Don't forget to attach the ground pins too! Following Figure 9 of the data sheet showing bidirectional motor control, connect the appropriate H-bridge outputs to the two terminals of your gearmotor. Put a 0.1uF unpolarized capacitor (e.g., an orange ceramic cap instead of a blue electrolytic "can" cap) across the terminals of your motor to reduce electrical noise due to your motor. |
||
| ⚫ | <li> Send these two signals (original and inverted) to inputs 2 and 7 of an [[media:L293.pdf|L293B H-bridge]]. Make sure this H-bridge chip is correctly powered by attaching +5V to the Vss pin (the "logic" power supply) and the battery's +7.2V to the Vs pin (the motor power supply). Don't forget to attach the ground pins too! Following Figure 9 of the data sheet showing bidirectional motor control, connect the appropriate H-bridge outputs to the two terminals of your gearmotor. Put a 0.1uF unpolarized capacitor (e.g., an orange ceramic cap instead of a blue electrolytic "can" cap) across the terminals of your motor to reduce electrical noise due to your motor. You should also use 4 "flyback" diodes, e.g. 1N4001's, to protect your H-bridge transistors from large reverse transients, as shown in Figure 9. (If you don't bother to do it, your circuit will likely still work, just be forewarned that this is bad practice! If you want to eliminate these extra components, you could use an [[media:L293D.pdf|L293D H-bridge chip]], which has the flyback diodes built in. The L293D has a lower current capacity, but sufficient for this exercise. See also this [http://www.mcmanis.com/chuck/robotics/tutorial/h-bridge/index.html nice tutorial] on building H-bridges from discrete components.) Now demonstrate that you can control the speed and direction of the motor by changing the duty cycle of your square wave signal. If you generate this square wave signal with your microcontroller instead, you now have bidirectional variable speed control of your motor. Make sure you understand the truth table in Figure 9. If you look at the two outputs of the H-bridge, you'll see noisy signals that look something like below. |
||
<br clear=all> |
<br clear=all> |
||
[[Image:H-bridge-outs-small.jpg]] |
|||
</ol> |
</ol> |
||
Latest revision as of 00:15, 14 February 2008
Note: this page describes one of two ways of doing PWM. This way uses two PWM signals inverse to each other. The other way uses one PWM signal and a DC level. See Pulse_width_modulation
Before doing this exercise, read about Brushed DC Motors and Driving Using Pulse Width Modulation. In this exercise you will use a function generator to create the pulse width modulation (PWM) signal that controls the motor. This simulates a signal that could be generated by a microcontroller.
Make sure your 7.2V battery pack is charged. The steps below assume you are using this gearmotor, which has a 224:1 gearhead and a stall torque of 50 oz-in at 5V, with a stall current of 600 mA.
- Use a function generator to create a 5 kHz square wave between 0V (GND) and 5V. Verify that you have done this by looking at the signal on an oscilloscope. (Note: In the figures below, I used a 20 kHz square wave, an unnecessarily high switching frequency for this exercise.) To learn how to do this with the function generator and oscilloscopes in the Mechatronics Lab, read the manuals on the Tektronix CFG253 Function Generator and Tektronix TDS220 Oscilloscope. Looking at the oscilloscope signal, vary the duty cycle (the percentage of time the signal is "high" each cycle) of the signal using the symmetry knob, say from 20% to 80%. Your oscilloscope should look something like the figures below.
- Attach your battery pack to your breadboard. Use your 7805 1A 5V voltage regulator so that you have 5V and 7.2V (with respect to the ground pin of the voltage regulator) available for use. Verify using your multimeter or an oscilloscope. (In my case, I measured about 5.2V and 9.5V.) Make sure your function generator ground is connected to the ground pin of the voltage regulator. Note: Don't try to jam the 7805 leads into a protoboard, as they are too large. Solder 22 AWG solid wires to the leads instead.
- Use a 74HC04 Hex Inverter/Buffer to get an inverted version of the function generator signal, in addition to the original signal. (Don't forget to power this chip!) Verify by looking at both the original signal and the inverted signal simultaneously on the oscilloscope. You should see something like below:
- Send these two signals (original and inverted) to inputs 2 and 7 of an L293B H-bridge. Make sure this H-bridge chip is correctly powered by attaching +5V to the Vss pin (the "logic" power supply) and the battery's +7.2V to the Vs pin (the motor power supply). Don't forget to attach the ground pins too! Following Figure 9 of the data sheet showing bidirectional motor control, connect the appropriate H-bridge outputs to the two terminals of your gearmotor. Put a 0.1uF unpolarized capacitor (e.g., an orange ceramic cap instead of a blue electrolytic "can" cap) across the terminals of your motor to reduce electrical noise due to your motor. You should also use 4 "flyback" diodes, e.g. 1N4001's, to protect your H-bridge transistors from large reverse transients, as shown in Figure 9. (If you don't bother to do it, your circuit will likely still work, just be forewarned that this is bad practice! If you want to eliminate these extra components, you could use an L293D H-bridge chip, which has the flyback diodes built in. The L293D has a lower current capacity, but sufficient for this exercise. See also this nice tutorial on building H-bridges from discrete components.) Now demonstrate that you can control the speed and direction of the motor by changing the duty cycle of your square wave signal. If you generate this square wave signal with your microcontroller instead, you now have bidirectional variable speed control of your motor. Make sure you understand the truth table in Figure 9. If you look at the two outputs of the H-bridge, you'll see noisy signals that look something like below.