PIC32MX: SPI EEPROM
Original Assignment
Do not erase this section!
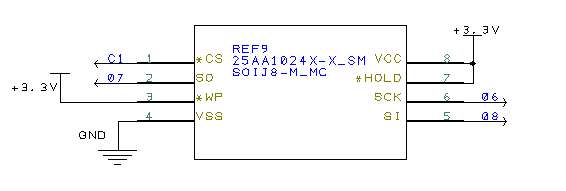
Your assignment is to interface to the SPI 25AA1024 EEPROM chip.
Overview
EEPROM stands for stands for Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory. It is a type of non-volitile memory that can be used to store little bits of data. Data will remain on EEPROM when power is disconnected, (like an external hardrive). The EEPROM chip must be reprogrammed in its entirety, and has a life span in the tens or hundreds of thousands of read/writes.
You can use the PIC32 to communicate with an EEPROM chip using SPI. This page refers to the usage of a Serial EEPROM.
To test that the code data was writing and reading correctly, the attached code sends data to the EEPROM through SPI, then from the EEPROM back to the PIC, and out to a LED display screen.
EEPROM vs. Flash memory: The EEPROM erases the cell one by one, and only erases the 1's back to zero. Flash erases the whole block at once. Since erasing causes wear to the cell, the EEPROM will have a slightly longer lifetime.
Circuit
Include a schematic and give any part numbers. A photo of your circuit is OK, but not as a replacement for a schematic.
Connection schematic for 25AA1024 chip
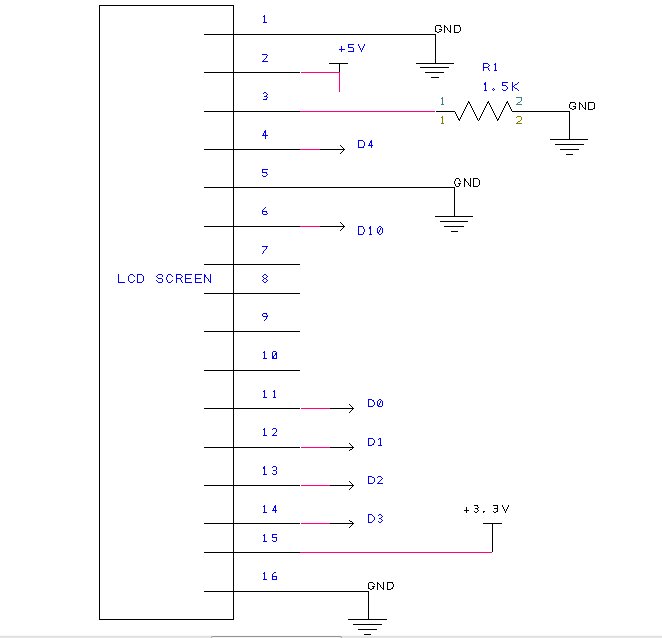
For visual feedback the PIC32 was connected to and LCD screen(1602A1 USB-A/Mini-B5-06):
Timing
Communication speed is determined by the clock signal and the Baud rate register (BRG).
There is a delay of about 50 us when writing using the SpiChnPutC function, otherwise it will send/recieve one bit per clock cycle. Overall timing is limited by the EEPROM's internal write cycle (on the order of 1 ms).
Code
Where possible, make it a single piece of well-commented cut-and-pastable code, or at least make each function that way, so others can easily copy it. Most comments should be in the code itself; outside the code (on the wiki) should only be explanatory comments that are too cumbersome to include in the code.
// This code checks the writing and reading of an EEPROM via SPI communication. Note: using this
code, one can verify using the scope that the EEPROM can actually be read and the read content is just
what is written into.
//this code also tells us that the transition between "write" and "read" is big. As a clock pulse is about
several us(even with prescaler set to 1024), the transition is about ms. So in this case,
//if new data is written, and you read it soon afterwards(us), the EEPROM will not respond.
//note: lines of code like "//int mData=SPI2STAT;" is used to read the status register to debug
#include "Compiler.h"
#include "HardwareProfile.h"
#include <plib.h>
#include "LCD.h"
#define chipselect LATCbits.LATC1
//manipulate /CS of EEPROM. Manipulation of EEPROM cannot be done by linking /SS of PIC and /CS of ROM. One
can check this with a scope: built-in functions like SpiChnPutc() does not generate corresponding
chipselect signal
int main()
{
lcd_init();
mInitAllLEDs();
LATC |= 0b0000000000000010; //Use C1 of PIC to toggle /CS of ROM
TRISC &=0b1111111111111101; //intialize C1 as output
TRISGbits.TRISG7=1;// set G7 as digital input
char LCDbuffer[33]; // this will store the string for the LCD
int ENA= 0b00000110; //ROM write-enable instruction
int INS1=0b00000010; //ROM write instruction
int add1=0x00; //address byte 1
int add2=0x11; //address byte 2
int add3=0xee; //address byte 3
int INS2=0b00000011; //ROM read instruction
int INS3=0b00000101; //read status register
int DIS = 0b00000100; //write disable sequence
while(1) //include a while loop to examine with a scope(cannot run single when there is
5ms time lag)
{
IEC0CLR=0x03800000; //disable all interrupts
SPI2CON = 0; //resets SPI2
int dump=SPI2BUF; //clears the receive buffer
IFS0CLR=0x03800000; //clear any existing event
SPI2STATCLR=0x40; //clears overflow flag
SpiChnOpen(2,SPI_CON_MSTEN| SPI_CON_MODE8|SPI_CON_ON, 1024); // divide fpb by 1024, configure the I/O
ports.
//there is another way to open SPI channel, but essentially the same, intialize the SFRs
Delayus(50);
chipselect=0; //enable chip. the ROM starts up with /CS high
SpiChnPutC(2,ENA);
Delayus(100); //give enough time for the previous instruction to get executed
chipselect=1; //toggle /CS to properly set write enable, demanded by the ROM
Delayus(50);
Delayus(30);
chipselect=0; //enable chip again to initiate write sequence
Delayus(50);
SpiChnPutC(2,INS1);
SpiChnPutC(2,add1);
SpiChnPutC(2,add2);
SpiChnPutC(2,add3);
SpiChnPutC(2,0x50); //the previous five instructions writed byte 0x50 to address(1+2+3)
Delayus(200); // delay long enough for the sequence to be fully executed
chipselect=1; //deselect the chip to enable internal write sequence which is surprisingly slow!!
Delayus(5000); //yes! believe your eyes, 5ms. otherwise the chip would be 'busy' so that the following
read sequence is 'dumped'
chipselect=0; //select chip to initiate reading
Delayus(50);
SpiChnPutC(2,INS2);
//reading instruction
SpiChnPutC(2,add1);
SpiChnPutC(2,add2);
SpiChnPutC(2,add3);
//read sequence, to read the very place where data was written
//int mData=SPI2STAT;//841 if put here
SpiChnPutC(2,0x00) //this line is necessary since the ROM needs clock signal to clock out the data.
//the reset of this code is hardly necessary for one to observe the write and read is executed. Because
using a scope, one can observe the data is clocked out of the EEPROM the moment the address is given(so
fast!)
//when this line is excuted, the data is put onto the SDI pins of PIC and as one bit is shifted out of
SDO, a new bit is shifted into SDI
//int mData=SPI2STAT; //841 here
while(SPI2STAT!=0x849){} //wait until the TX buffer is empty, and enable data storage by clearing overflow
flag!!!without this line, one can get only 0xff
//int mData=SPI2STAT; //849 here, transmit is empty
SPI2STATCLR = 0x40; //clear overflow flag
int receive = SPI2BUF; //since overflow is cleared, buffer is read so that new data can
come in
//int mData=SPI2STAT; //808 here: busy and buffer is cleared, new data should be waiting to come in
Delayus(500);
int mData=SPI2STAT; //9 here,
receive = SPI2BUF; //read
Delayus(200);
chipselect=1; //end of reading sequence
sprintf(LCDbuffer, "\f%c", receive); // make the string 0x50 represents "P" in ASCII
putsLCD(LCDbuffer); // write the contents of the variable
}
}
This section of code is used to read and write strings of data to the EEPROM
//this code does string transmission
#include "Compiler.h"
#include "HardwareProfile.h"
#include <plib.h>
#include "LCD.h"
#define chipselect LATCbits.LATC1
//manipulate /CS of EEPROM. Manipulation of EEPROM cannot be done by //linking /SS of PIC and /CS of ROM. One can check this with a scope: //built-in functions like SpiChnPutc() does not generate corresponding //chipselect signal
//function declaration
//void string(char *A,int s);
//this function does string, int s indicates the size of the string int here;
int ENA= 0b00000110; //ROM write-enable instruction
int INS1=0b00000010; //ROM write instruction
int INS2=0b00000011; //ROM read instruction
void write(unsigned char *data, int length); //actually address is 3-byte long but the first 7 bit dose not matter, we just make the first 8bit to be all 0s
void read(unsigned char *edata, int length);
int main()
{
lcd_init();
mInitAllLEDs();
LATC |= 0b0000000000000010; //Use C1 of PIC to toggle /CS of ROM
TRISC &=0b1111111111111101; //intialize C1 as output
TRISGbits.TRISG7=1;// set G7 as digital input
char LCDbuffer[33]; // this will store the string for the LCD
short addr=0x0000; //initial writing address, first byte is set to zero and not displayed
IEC0CLR=0x03800000; //disable all interrupts
SPI2CON = 0; //resets SPI2
int dump=SPI2BUF; //clears the receive buffer
IFS0CLR=0x03800000; //clear any existing event
SPI2STATCLR=0x40; //clears overflow flag
SpiChnOpen(2,SPI_CON_MSTEN| SPI_CON_MODE8|SPI_CON_ON, 1024); // divide fpb by 1024, configure the I/O ports.
unsigned char string[]="SPI SUCKS!!";
int size=sizeof(string);
unsigned char readstring[size];
//writing block, first enable writing
Delayus(50);
chipselect=0; //enable chip. the ROM starts up with /CS high
SpiChnPutC(2,ENA);
Delayus(100); //give enough time for the previous instruction to get executed
chipselect=1; //toggle /CS to properly set write enable, demanded by the ROM
Delayus(50);
Delayus(30);
chipselect=0;
write(string, size);
chipselect=1;
Delayus(5000);
//delay a long time for those data to get written, internal writ cycle
/***
Below is the reading part
***/
chipselect=0; //select chip to initiate reading
read(readstring,size);
chipselect=1;
//terminate reading sequence
sprintf(LCDbuffer, "\f%s", readstring); // make the string 0x50 represents "P" in ASCII
putsLCD(LCDbuffer); // write the contents of the variable
}
//functions
void write(unsigned char *edata, int length)
{
// Send Data to eeprom to program one location
Delayus(50);
SpiChnPutC(2,INS1); //enable the chip and write "write" instruction
SpiChnPutC(2,0x00); //the first 8-bit address
SpiChnPutC(2,0x11);
SpiChnPutC(2,0x11);
while(length)
{
SpiChnPutC(2,*edata);
edata++;
length--;
}
Delayus(20000); // delay long enough for the sequence to be fully executed
}
//below is the function that does sequential read
void read(unsigned char *data, int length)
{
// Send Data to eeprom to program one location
Delayus(50);
SpiChnPutC(2,INS2); //enable the chip and write "read" instruction
SpiChnPutC(2,0x00); //the first 8-bit address
SpiChnPutC(2,0x11);
SpiChnPutC(2,0x11); //write the starting address
SpiChnPutC(2,0x00);
while(SPI2STAT!=0x849){} //wait until the TX buffer is empty, and enable data storage by clearing overflow flag!!!
SPI2STATCLR = 0x40; //clear overflow flag
int receive = SPI2BUF; //since overflow is cleared, buffer is read so that new data can come in
Delayus(500);
receive = SPI2BUF; //read
*data=receive;
data++;
length--;
//here=SPI2STAT; //008 here, means transmit buffer is empty
while(length)
{
SpiChnPutC(2,0x00);
Delayus(500);
receive = SPI2BUF; //read
*data=receive;
data++;
length--;
}
Delayus(5000);
}
Debugging
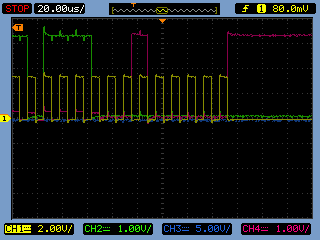
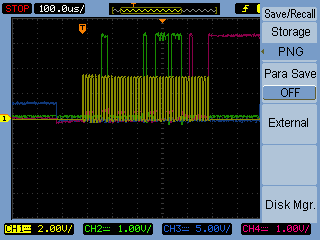
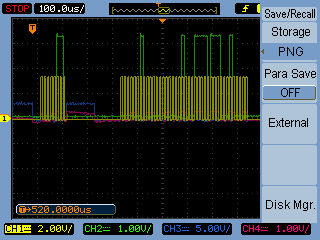
If the readout on the LCD screen is not what was expected connect the EEPROM chip to a four channel oscilloscope and double check whether the data is being correctly transferred. For example: the yellow channel 1 is clock signal, green channel 2 is PIC data output, blue channel 3 is /CS, purple channel 4 is pic data input
closed look at the EEPROM's output