PPOD-mini: 6-DOF Shaker
Team Members
- Ankur Bakshi (Biomedical Engineering, Class of 2009)
- Donald Redding (Mechanical Engineering, Class of 2009)
- Ben Tollberg (Mechanical Engineering, Class of 2009)
Introduction
The PPOD-mini is a miniaturized version of the Programmable Part-feeding Oscillatory Device (PPOD) found in the Laboratory for Intelligent Mechanical Systems (LIMS) at Northwestern. The PPOD-mini utilizes six speakers that act like actuators. The speakers are connected to an acrylic plate via flexures of tygon and iron. In its current implementation, the phase of the speakers can be controlled independently, giving the device six degrees of freedom. The movement of objects placed on the acrylic plate can be controlled by changing the phases of the speakers.
The PPOD mini measures about 12" x 12" x 8" (length x width x height) and can be plugged into a wall outlet for power. The design utilizes a switch to start the speaker-phase changing algorithm, a keypad for input to change the speaker phases, and an 16x2 line LCD for user interfacing and to output the speaker phases. A PIC 18f4520 provides the computing power. Each speaker is driven by an H-bridge (1 L293D runs two speakers), which is powered by a 10W power supply from Marlin Jones ([1]). The speakers are 1W, 16 ohm speakers from Jameco.
Operation
When first plugging in the PPOD-mini, the switch to change the speaker's phase is triggered and the text on the LCD is garbled. At this point, we are not sure why this occurs. By pressing the reset button on the PIC board or by pressing buttons on the keypad until readable text appears. To change the phase of a speaker, the switch must be pressed. Then following the instructions on the LCD, press the a number between one and six to select the speaker. Next, press a number between zero and five to choose a phase from 0-300 degrees in 60 degree increments. The increments can be changed by uploading a new program to the PIC. The speakers should then be running.
Due to mechanical issues, we were not able to produce many patterns. Most patterns were only clear near the edges of the plate, as the speaker's did not produce displacements at the center of the plate. A circular pattern was observed by putting the speakers all out of phase. The speakers were set to 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 for speakers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 respectively. A video of this pattern can be seen here. Another somewhat observable pattern involved setting two pairs of nodes (e.g. speakers 1 and 6 and speakers 2 and 3) to phase 0 and the other node (e.g. speakers 4 and 5) to phase 5. This resulted in movement towards speakers 4 and 5. A video of this pattern can be seen here.
Mechanical Design
The PPOD consists of a circular plate mounted via flexible supports to six speakers. The six speakers are mounted in a circle on a base plate.
Speakers
The speakers used were 89 db speakers from Jameco ([2]). The speaker's output capabilities were tested using an accelerometer. Without any weight attached, the speakers produced 1.3 g's acceleration at 50 hz. However, under the load of the plate, we found that the speakers gave the maximum acceleration at 30 hz.
Speaker Mounts
The speaker mounts are made of lightweight wood. The side of the mount which the speaker sits in is a 4" x 4" square. A circular hole is cut into the middle of this face to allow the speaker to fit in the mount. This face is elevated 30 degrees from the horizontal. There are two triangular sides on the speaker mount to achieve this angle. The height of the triangular sides is 2" and the base is 3.46" (30-60-90 triangle).
Vibrating Plate Supports
The supports connecting the vibrating plate to the speakers is made of flexible plastic tubing. The tubing is approximately 1/4" in diameter. To connect the tubing to the speakers, a hot glue gun was used. In order to ensure that the speakers are transmitting vibrations via the connections, a short piece of 1/4" threaded rod was placed in the middle of the tubing to increase the rigidity of the connection. This is done with one end of the rod stuck in to the tubing connected to the speaker. The other end of the rod is connected to another piece of tubing. This second piece of tubing goes to the vibrating plate.
Vibrating Plate
The vibrating plate is circular and acrylic plastic. The diameter of this plate is 8". In order to connect the plate to the tubing, 6 holes are drilled equally spaced on a circle around the plate approximately half an inch from the plate's outer edge. Again 1/4" diameter screws are used to connect the tubing. The screws are fed down through the plate and into the second piece of tubing. Hot glue was used as necessary on the plate around the screws to ensure that the screws are held in place. Doing so ensures the vibration is transmitted from the speakers to the plate.
Circuitry Housing
The electronics is housed under the baseboard the speaker is mounted to, which is a 12" by 12" piece of black ABS plastic. The baseboard sits on a wooden platform consisting of three rectangular sides of size 4"x12". It is constructed so that the baseboard is elevated 4". The platform sides are connected using hot glue and connected to the baseboard using hot glue. Holes are drilled in the sides of the platform to feed the speaker wire through. A fourth side is then added to the platform. The LCD and keypad are mounted to this fourth side. The electronics are mounted to the underside of the baseboard and are concealed by the wooden platform.
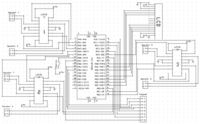
Circuit Diagram
To the right is the complete circuit schematic for our project. The +5V and GND for the L293D chips were supplied by the external power supply. The LCD was powered by the PIC +5V and GND in order to avoid some overheating issues that occurred when they were connected to the external supply. Each L293D chip controlled two speakers, with one full H-bridge for each speaker. The direction that voltage is applied to each speaker is controlled by the high or low signals that are output from the PIC to the H-bridges. A push button is connected to the external +5V and RB0 on the PIC to trigger the external interrupt in the code.
Code
The following is our main program code that was put on the PIC. The files flex_lcd.c and key.c must be included in the same folder to correctly operate the keypad and LCD. Our modified versions of those files are also included in this section. The key.c code was adapted from code posted here.
Main Code
//Ankur Bakshi, Donnie Redding, Ben Tollberg
//Group 23: PPOD-mini: 6-DOF Shaker
#include <18f4520.h>
#fuses HS,NOLVP,NOWDT
#use delay (clock=40000000)
#include "key.c" //keypad file
#include "flex_lcd.c" //lcd file
int32 frequency = 40; //Set speaker frequency in hertz, this is the one we used in an attempt to
int ii; //maximize the acceleration of the speakers
int32 halfperiod;
int32 delays;
int8 s_p[6]={0,0,0,0,0,0}; //Array that will hold the phase of each speaker
char k;
#INT_EXT
void INT0isr() { //Interrupt routine is called when Pin RB0 goes from low to high
//which occurs when the red button is pressed and released
int s;
int flag=1;
char speaker;
char phase;
int i, j, temp;
printf(lcd_putc,"\fChanging Phase");
delay_ms(10);
printf(lcd_putc,"\n\fSpeaker Number:");
while(flag==1){ //Loop will repeat until acceptable input is pressed
speaker = kbd_getc(); //Read speaker number from keypad
if(speaker!=0) { //Determine speaker
printf(lcd_putc,"%c",speaker);
switch (speaker){
case '1':
s=0;
flag=0; //Exits loop if acceptable input is entered
break;
case '2':
s=1;
flag=0;
break;
case '3':
s=2;
flag=0;
break;
case '4':
s=3;
flag=0;
break;
case '5':
s=4;
flag=0;
break;
case '6':
s=5;
flag=0;
break;
default:
printf(lcd_putc,"\n\fInvalid input.");
delay_ms(10);
printf(lcd_putc,"\n\nSpeaker Number:");
break;
}
}
}
flag=1;
printf(lcd_putc,"\nEnter Phase:");
while(flag==1){ //Loop repeats until acceptable input is pressed
phase = kbd_getc(); //Reads in phase from keypad
if(phase!=0) {
printf(lcd_putc,"%c",phase);
switch (phase){ //Set phase array
case '0':
s_p[s]=0;
flag=0;
break;
case '1':
s_p[s]=1;
flag=0;
break;
case '2':
s_p[s]=2;
flag=0;
break;
case '3':
s_p[s]=3;
flag=0;
break;
case '4':
s_p[s]=4;
flag=0;
break;
case '5':
s_p[s]=5;
flag=0;
break;
default:
printf(lcd_putc,"\nInvalid input.");
delay_ms(10);
printf(lcd_putc,"\nEnter Phase:");
break;
}
}
}
}
void main (){
enable_interrupts(INT_EXT); //Enables external interrupts
enable_interrupts(GLOBAL);
ext_int_edge(0, L_TO_H); //Sets external interrupt to trigger when RB0 goes from
//low to high
halfperiod = 500000/frequency; //Converts frequency in hertz to half of the period
//in microseconds
delays = halfperiod/3; //Sets delays to one-sixth of a full period, for a 60 degree
//phase shift
lcd_init();
kbd_init(); //initialize keypad
printf(lcd_putc,"Starting...\n");
delay_ms(1000);
printf(lcd_putc,"\n");
while(true) { //This function sets the speakers high or low based on
if(s_p[0] == 0){ //the information saved in the phase array s_p. It checks
output_high(PIN_A0); //to see which speakers are supposed to be changed at
output_low(PIN_A1); //a certain time, waits for a time that equates to 60
} //degrees of phase shift and checks again. Changing which
if(s_p[1] == 0){ //pin is high and which is low changes the direction of
output_high(PIN_A2); //the voltage across the speakers.
output_low(PIN_A3);
}
if(s_p[2] == 0){
output_high(PIN_A4);
output_low(PIN_A5);
}
if(s_p[3] == 0){
output_high(PIN_C6);
output_low(PIN_E0);
}
if(s_p[4] == 0){
output_high(PIN_E1);
output_low(PIN_E2);
}
if(s_p[5] == 0){
output_high(PIN_C5);
output_low(PIN_D0);
}
if(s_p[0] == 3){
output_low(PIN_A0);
output_high(PIN_A1);
}
if(s_p[1] == 3){
output_low(PIN_A2);
output_high(PIN_A3);
}
if(s_p[2] == 3){
output_low(PIN_A4);
output_high(PIN_A5);
}
if(s_p[3] == 3){
output_low(PIN_C6);
output_high(PIN_E0);
}
if(s_p[4] == 3){
output_low(PIN_E1);
output_high(PIN_E2);
}
if(s_p[5] == 3){
output_low(PIN_C5);
output_high(PIN_D0);
}
delay_us(delays);
if(s_p[0] == 1){
output_high(PIN_A0);
output_low(PIN_A1);
}
if(s_p[1] == 1){
output_high(PIN_A2);
output_low(PIN_A3);
}
if(s_p[2] == 1){
output_high(PIN_A4);
output_low(PIN_A5);
}
if(s_p[3] == 1){
output_high(PIN_C6);
output_low(PIN_E0);
}
if(s_p[4] == 1){
output_high(PIN_E1);
output_low(PIN_E2);
}
if(s_p[5] == 1){
output_high(PIN_C5);
output_low(PIN_D0);
}
if(s_p[0] == 4){
output_low(PIN_A0);
output_high(PIN_A1);
}
if(s_p[1] == 4){
output_low(PIN_A2);
output_high(PIN_A3);
}
if(s_p[2] == 4){
output_low(PIN_A4);
output_high(PIN_A5);
}
if(s_p[3] == 4){
output_low(PIN_C6);
output_high(PIN_E0);
}
if(s_p[4] == 4){
output_low(PIN_E1);
output_high(PIN_E2);
}
if(s_p[5] == 4){
output_low(PIN_C5);
output_high(PIN_D0);
}
delay_us(delays);
if(s_p[0] == 2){
output_high(PIN_A0);
output_low(PIN_A1);
}
if(s_p[1] == 2){
output_high(PIN_A2);
output_low(PIN_A3);
}
if(s_p[2] == 2){
output_high(PIN_A4);
output_low(PIN_A5);
}
if(s_p[3] == 2){
output_high(PIN_C6);
output_low(PIN_E0);
}
if(s_p[4] == 2){
output_high(PIN_E1);
output_low(PIN_E2);
}
if(s_p[5] == 2){
output_high(PIN_C5);
output_low(PIN_D0);
}
if(s_p[0] == 5){
output_low(PIN_A0);
output_high(PIN_A1);
}
if(s_p[1] == 5){
output_low(PIN_A2);
output_high(PIN_A3);
}
if(s_p[2] == 5){
output_low(PIN_A4);
output_high(PIN_A5);
}
if(s_p[3] == 5){
output_low(PIN_C6);
output_high(PIN_E0);
}
if(s_p[4] == 5){
output_low(PIN_E1);
output_high(PIN_E2);
}
if(s_p[5] == 5){
output_low(PIN_C5);
output_high(PIN_D0);
}
delay_us(delays);
if(s_p[0] == 3){
output_high(PIN_A0);
output_low(PIN_A1);
}
if(s_p[1] == 3){
output_high(PIN_A2);
output_low(PIN_A3);
}
if(s_p[2] == 3){
output_high(PIN_A4);
output_low(PIN_A5);
}
if(s_p[3] == 3){
output_high(PIN_C6);
output_low(PIN_E0);
}
if(s_p[4] == 3){
output_high(PIN_E1);
output_low(PIN_E2);
}
if(s_p[5] == 3){
output_high(PIN_C5);
output_low(PIN_D0);
}
if(s_p[0] == 0){
output_low(PIN_A0);
output_high(PIN_A1);
}
if(s_p[1] == 0){
output_low(PIN_A2);
output_high(PIN_A3);
}
if(s_p[2] == 0){
output_low(PIN_A4);
output_high(PIN_A5);
}
if(s_p[3] == 0){
output_low(PIN_C6);
output_high(PIN_E0);
}
if(s_p[4] == 0){
output_low(PIN_E1);
output_high(PIN_E2);
}
if(s_p[5] == 0){
output_low(PIN_C5);
output_high(PIN_D0);
}
delay_us(delays);
if(s_p[0] == 4){
output_high(PIN_A0);
output_low(PIN_A1);
}
if(s_p[1] == 4){
output_high(PIN_A2);
output_low(PIN_A3);
}
if(s_p[2] == 4){
output_high(PIN_A4);
output_low(PIN_A5);
}
if(s_p[3] == 4){
output_high(PIN_C6);
output_low(PIN_E0);
}
if(s_p[4] == 4){
output_high(PIN_E1);
output_low(PIN_E2);
}
if(s_p[5] == 4){
output_high(PIN_C5);
output_low(PIN_D0);
}
if(s_p[0] == 1){
output_low(PIN_A0);
output_high(PIN_A1);
}
if(s_p[1] == 1){
output_low(PIN_A2);
output_high(PIN_A3);
}
if(s_p[2] == 1){
output_low(PIN_A4);
output_high(PIN_A5);
}
if(s_p[3] == 1){
output_low(PIN_C6);
output_high(PIN_E0);
}
if(s_p[4] == 1){
output_low(PIN_E1);
output_high(PIN_E2);
}
if(s_p[5] == 1){
output_low(PIN_C5);
output_high(PIN_D0);
}
delay_us(delays);
if(s_p[0] == 5){
output_high(PIN_A0);
output_low(PIN_A1);
}
if(s_p[1] == 5){
output_high(PIN_A2);
output_low(PIN_A3);
}
if(s_p[2] == 5){
output_high(PIN_A4);
output_low(PIN_A5);
}
if(s_p[3] == 5){
output_high(PIN_C6);
output_low(PIN_E0);
}
if(s_p[4] == 5){
output_high(PIN_E1);
output_low(PIN_E2);
}
if(s_p[5] == 5){
output_high(PIN_C5);
output_low(PIN_D0);
}
if(s_p[0] == 2){
output_low(PIN_A0);
output_high(PIN_A1);
}
if(s_p[1] == 2){
output_low(PIN_A2);
output_high(PIN_A3);
}
if(s_p[2] == 2){
output_low(PIN_A4);
output_high(PIN_A5);
}
if(s_p[3] == 2){
output_low(PIN_C6);
output_high(PIN_E0);
}
if(s_p[4] == 2){
output_low(PIN_E1);
output_high(PIN_E2);
}
if(s_p[5] == 2){
output_low(PIN_C5);
output_high(PIN_D0);
}
delay_us(delays);
printf(lcd_putc,"\n\fPhases:%i%i%i%i%i%i\n",s_p[0],s_p[1],s_p[2],s_p[3],s_p[4],s_p[5]);
}
}
LCD Code
// flex_lcd.c
// These pins were originally set for D0-D6, we changed them to fit
// our needs.
#define LCD_DB4 PIN_D1
#define LCD_DB5 PIN_D2
#define LCD_DB6 PIN_D3
#define LCD_DB7 PIN_D4
#define LCD_RS PIN_D5
#define LCD_RW PIN_D6
#define LCD_E PIN_D7
// If you only want a 6-pin interface to your LCD, then
// connect the R/W pin on the LCD to ground, and comment
// out the following line.
#define USE_LCD_RW 1
//========================================
#define lcd_type 2 // 0=5x7, 1=5x10, 2=2 lines
#define lcd_line_two 0x40 // LCD RAM address for the 2nd line
int8 const LCD_INIT_STRING[4] =
{
0x20 | (lcd_type << 2), // Func set: 4-bit, 2 lines, 5x8 dots
0xc, // Display on
1, // Clear display
6 // Increment cursor
};
//-------------------------------------
void lcd_send_nibble(int8 nibble)
{
// Note: !! converts an integer expression
// to a boolean (1 or 0).
output_bit(LCD_DB4, !!(nibble & 1));
output_bit(LCD_DB5, !!(nibble & 2));
output_bit(LCD_DB6, !!(nibble & 4));
output_bit(LCD_DB7, !!(nibble & 8));
delay_cycles(1);
output_high(LCD_E);
delay_us(2);
output_low(LCD_E);
}
//-----------------------------------
// This sub-routine is only called by lcd_read_byte().
// It's not a stand-alone routine. For example, the
// R/W signal is set high by lcd_read_byte() before
// this routine is called.
#ifdef USE_LCD_RW
int8 lcd_read_nibble(void)
{
int8 retval;
// Create bit variables so that we can easily set
// individual bits in the retval variable.
#bit retval_0 = retval.0
#bit retval_1 = retval.1
#bit retval_2 = retval.2
#bit retval_3 = retval.3
retval = 0;
output_high(LCD_E);
delay_cycles(1);
retval_0 = input(LCD_DB4);
retval_1 = input(LCD_DB5);
retval_2 = input(LCD_DB6);
retval_3 = input(LCD_DB7);
output_low(LCD_E);
return(retval);
}
#endif
//---------------------------------------
// Read a byte from the LCD and return it.
#ifdef USE_LCD_RW
int8 lcd_read_byte(void)
{
int8 low;
int8 high;
output_high(LCD_RW);
delay_cycles(1);
high = lcd_read_nibble();
low = lcd_read_nibble();
return( (high<<4) | low);
}
#endif
//----------------------------------------
// Send a byte to the LCD.
void lcd_send_byte(int8 address, int8 n)
{
output_low(LCD_RS);
#ifdef USE_LCD_RW
while(bit_test(lcd_read_byte(),7)) ;
#else
delay_us(60);
#endif
if(address)
output_high(LCD_RS);
else
output_low(LCD_RS);
delay_cycles(1);
#ifdef USE_LCD_RW
output_low(LCD_RW);
delay_cycles(1);
#endif
output_low(LCD_E);
lcd_send_nibble(n >> 4);
lcd_send_nibble(n & 0xf);
}
//----------------------------
void lcd_init(void)
{
int8 i;
output_low(LCD_RS);
#ifdef USE_LCD_RW
output_low(LCD_RW);
#endif
output_low(LCD_E);
delay_ms(15);
for(i=0 ;i < 3; i++)
{
lcd_send_nibble(0x03);
delay_ms(5);
}
lcd_send_nibble(0x02);
for(i=0; i < sizeof(LCD_INIT_STRING); i++)
{
lcd_send_byte(0, LCD_INIT_STRING[i]);
// If the R/W signal is not used, then
// the busy bit can't be polled. One of
// the init commands takes longer than
// the hard-coded delay of 60 us, so in
// that case, lets just do a 5 ms delay
// after all four of them.
#ifndef USE_LCD_RW
delay_ms(5);
#endif
}
}
//----------------------------
void lcd_gotoxy(int8 x, int8 y)
{
int8 address;
if(y != 1)
address = lcd_line_two;
else
address=0;
address += x-1;
lcd_send_byte(0, 0x80 | address);
}
//-----------------------------
void lcd_putc(char c)
{
switch(c)
{
case '\f':
lcd_send_byte(0,1);
delay_ms(2);
break;
case '\n':
lcd_gotoxy(1,2);
break;
case '\b':
lcd_send_byte(0,0x10);
break;
default:
lcd_send_byte(1,c);
break;
}
}
//------------------------------
#ifdef USE_LCD_RW
char lcd_getc(int8 x, int8 y)
{
char value;
lcd_gotoxy(x,y);
// Wait until busy flag is low.
while(bit_test(lcd_read_byte(),7));
output_high(LCD_RS);
value = lcd_read_byte();
output_low(lcd_RS);
return(value);
}
#endif
Keypad Code
//=============================
//Header pins go from 1-8 from left to right when looking at the keypad.
//The PIC pins being used can be changed depending on specific needs of a project.
//If not using the B pins for the rows, add pull up resistors
//Keypad connection:
#define row0 PIN_B1 //header pin 8
#define row1 PIN_B5 //header pin 1
#define row2 PIN_B3 //header pin 2
#define row3 PIN_B4 //header pin 4
#define col0 PIN_C0 //header pin 3
#define col1 PIN_C1 //header pin 5
#define col2 PIN_C2 //header pin 6
#define col3 PIN_C4 //header pin 7
// Keypad layout:
char const KEYS[4][4] =
{{'1','2','3','A'},
{'4','5','6','B'},
{'7','8','9','C'},
{'*','0','#','D'}};
#define KBD_DEBOUNCE_FACTOR 33 // Set this number to apx n/333 where
// n is the number of times you expect
// to call kbd_getc each second
void kbd_init()
{
//set_tris_b(0xF0);
//output_b(0xF0);
port_b_pullups(true);
}
short int ALL_ROWS (void)
{
if(input (row0) & input (row1) & input (row2) & input (row3))
return (0);
else
return (1);
}
char kbd_getc()
{
static byte kbd_call_count;
static short int kbd_down;
static char last_key;
static byte col;
byte kchar;
byte row;
kchar='\0';
if(++kbd_call_count>KBD_DEBOUNCE_FACTOR)
{
switch (col)
{
case 0:
output_low(col0);
output_high(col1);
output_high(col2);
output_high(col3);
break;
case 1:
output_high(col0);
output_low(col1);
output_high(col2);
output_high(col3);
break;
case 2:
output_high(col0);
output_high(col1);
output_low(col2);
output_high(col3);
break;
case 3:
output_high(col0);
output_high(col1);
output_high(col2);
output_low(col3);
break;
}
if(kbd_down)
{
if(!ALL_ROWS())
{
kbd_down=false;
kchar=last_key;
last_key='\0';
}
}
else
{
if(ALL_ROWS())
{
if(!input (row0))
row=0;
else if(!input (row1))
row=1;
else if(!input (row2))
row=2;
else if(!input (row3))
row=3;
last_key =KEYS[row][col];
kbd_down = true;
}
else
{
++col;
if(col==4)
col=0;
}
}
kbd_call_count=0;
}
return(kchar);
}
Issues with Design
A few issues with the design have been noted which should be taken into consideration by groups that may be working with this project in the future.
Mechanical Issues
The biggest issue right now is that two of the speakers are not vibrating with nearly as much amplitude as the other speakers. This irregularity has an effect on the expected movement of parts placed on the platform and makes these movements very hard to predict. The speakers function properly when removed from their mounts, so it appears that the problem is that the flexures are applying more force on these speakers, preventing them from moving very far. We found that it does not take much force to keep the speakers from fully vibrating.
Electrical Issues
The PPOD always acts a bit strangely when it is plugged in and the power strip is first turned on. The LCD sometimes displays random characters and the speakers may not run immediately. We have found that usually pressing a number on the keypad from 1-5 repeatedly will eventually return the system to normal. It appears to automatically enter the external interrupt loop when it first starts up for a few cycles. Once it returns to normal operation you may have to set the phase of the speakers back to zero as some of them may have changed. Also, if this does not immediately work pressing the reset button on the PIC board a few times also seems to help in some cases. We currently do not have an explanation for these errors.
Future Steps
As mentioned in the previous section, the all the speakers do not vibrate with the same force. There are several ways to deal with this issue. First, a little experimentation may need to be done with the flexures. The flexures may be too stiff, preventing the diaphragm of the speakers from fully vibrating. The next thing to do is to check the level of the plate and the geometry of the speakers and insertion points. If the mass of the plate is unevenly distributed, some speakers may have to apply more force than others. Since the speakers will inevitably output unequal forces, amplitude control will most likely be necessary. This can be achieved by place a potentiometer between a line from the H-bridge and the speaker. Given the weak output of some speakers at 5V, reducing amplitude may not be sufficient. Raising the power source to 7V and getting higher power speakers (for example [3]) will resolve this issue.
The original PPOD used feedback from six accelerometers to independently control the amplitude of each of the speakers. One possible method to implement a simpler system would be to use one accelerometer in the middle of the plate. When all the speakers are set in phase, there should be Y acceleration without X acceleration. However, if not all of the speakers are firing equally, there will be X acceleration. Based on the X acceleration, the node that is misfiring can be calculated.
During testing, it was noted that holding down a speaker diaphragm (effectively turning it off) caused distinct movements. If the speakers are not strong enough to cause movement, adding the ability to turn off individual speakers may be necessary.