Voltage and Current Dividers
Voltage Division
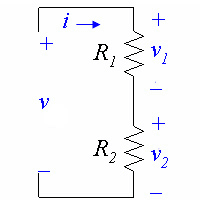
When we have a voltage across a string of resistors connected in series, the voltage across the entire string will be divided up among the resistors. We can express the voltage across a single resistor as a ratio of voltages and resistances, without ever knowing the current.
In the circuit above,
or
We can generalize this equation for resistors in series with the equation:
where is the voltage across resistor and is the voltage across the whole string of resistors.
Current Division
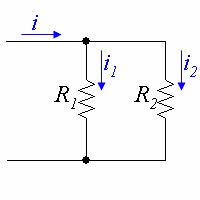
Resistors in parallel divide up the current. When we have a current flowing through resistors in parallel, we can express the current flowing through a single resistor as ratio of currents and resistances, without ever knowing the voltage.
In the circuit above
or
where is the current flowing through all the resistors. Note that the numerator on the right is R2, not R1. Remember that a larger resistance will carry a smaller current.
We can generalize the equation for resistors in parallel with the equation:
where is the current flowing through resistor and is the current flowing through all the resistors.
Practice Problems
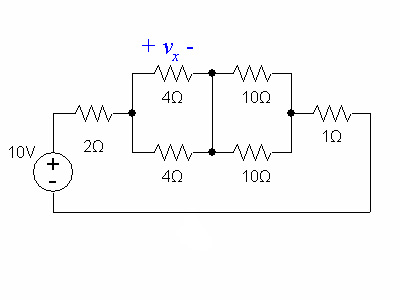
Problem 1
Use voltage division to find in the circuit below:
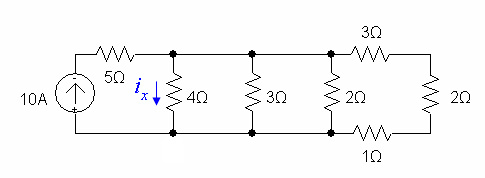
Problem 2
Simplify the circuit and then use current division to find in the circuit below: