Difference between revisions of "NU32: Using the dsPIC33FJ12MC201 QEI to SPI board"
NickMarchuk (talk | contribs) (New page: Using the dsPIC33FJ for quad decode == Overview == Why this chip == Details == The board == Library Functions == This code How to get the count The f...) |
|||
| (11 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''THIS PAGE REFERS TO A PRE-RELEASE VERSION OF THE NU32 PIC32 DEVELOPMENT BOARD. FOR INFORMATION, SAMPLE CODE, AND VIDEOS RELATED TO THE PRODUCTION VERSION (2016 AND LATER), AND TO THE CORRESPONDING BOOK "EMBEDDED COMPUTING AND MECHATRONICS WITH THE PIC32 MICROCONTROLLER," VISIT [[NU32|THE NU32 PAGE]].''' |
|||
Using the dsPIC33FJ for quad decode |
|||
Using the dsPIC33FJ12MC201 breakout board for quadrature decoding. |
|||
[[Image:NU32_dsPIC33FJ12MC201.jpg|thumb|200px|The dsPIC33FJ12MC201 breakout board|center]] |
|||
== Overview == |
== Overview == |
||
[[Media:dsPIC33FJ12MC201.pdf|Datasheet]], [http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/devicedoc/93002A.pdf Specifics on the QEI module] |
|||
Why this chip |
|||
The dsPIC series of PIC microcontrollers are inexpensive 16 bit microcontrollers, specializing in the ability do fast digital signal processing. |
|||
The dsPIC33FJ12MC201 is a low pin count chip that runs on 3.3V at 80MHz without an external oscillator. It has the ability to remap peripheral functionality to any pins (labeled RPx). It also has a special peripheral called QEI, or Quadrature Encoder Interface. The QEI module receives the quadrature square waves from an encoder and keeps track of the net motion of the encoder as a 16 bit unsigned integer. |
|||
== Details == |
== Details == |
||
The breakout board has been pre-programmed to read a quadrature signal on pins RP7 and RP8 (pins 11 and 12). It will keep track of the net motion of the encoder as a 16 bit integer, initializing to 32767. The dsPIC will report the 16 bit unsigned number over SPI communication when a '1' is sent. |
|||
The board |
|||
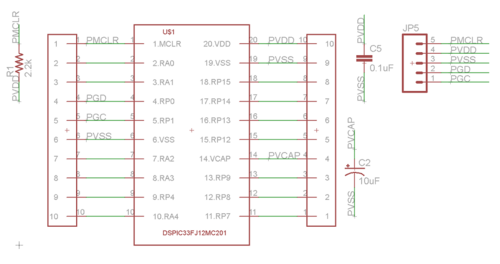
[[Image:NU32_dsPIC33FJ12MC201_sch.png|thumb|500px|The dsPIC33FJ12MC201 breakout board schematic|center]] |
|||
== Wiring == |
|||
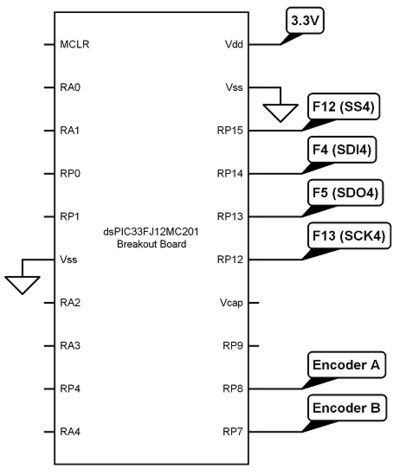
[[Image:NU32_dsPIC33FJ12MC201_wireup.png|thumb|400px|How to connect the dsPIC33FJ12MC201 breakout board to the PIC32|center]] |
|||
== Library Functions == |
== Library Functions == |
||
[[Media: |
[[Media:NU32_dsPIC_QEI_example.c | This code]] is an example of how to read the encoder count using the NU32. |
||
The functions are: |
The functions are: |
||
*void initEncoderSPI(void) - enables SPI4 as master at 8MHz |
|||
*void NU32_Initialize(void) - enables UART1 and UART4 at 115200 baud. UART4 starts with the interrupt at priority level 3, UART1 starts with no interrupt enabled |
|||
*int getEncoder(void) - sends a '1' to the dsPIC, returns the value returned by the dsPIC |
|||
*void NU32_EnableUART1Interrupt(void) - enables the UART1 interrupt |
|||
*void NU32_WriteUART1(const char *) - call with the character array you wish to send, make the array with sprintf() |
|||
*void NU32_ReadUART1(char *, int) - call with the array you want to read into, and the maximum size of the array. The code will wait at this function and buffer all characters received until you send a '\r' or '\n' (by pressing [enter] on your keyboard) |
|||
NU32_dsPIC_Example.c above demonstrates how to use the breakout board. |
|||
== Sample Code == |
== Sample Code == |
||
To initialize the |
To initialize the SPI communication, call initEncoderSPI(), : |
||
<pre> |
<pre> |
||
initEncoderSPI(); |
|||
</pre> |
</pre> |
||
To read the encoder count, call getEncoder(), : |
|||
To write a string to the computer, use NU32_WriteUART1(charArray). The special characters '\r' and '\n' are carriage return and newline. Using them together puts the cursor on the next line. |
|||
<pre> |
<pre> |
||
int count = getEncoder(); |
|||
NU32_WriteUART1("\r\nHello World!\r\n"); |
|||
</pre> |
</pre> |
||
To write a string with the value of a variable in it, use sprintf(charArray,"%d") and NU32_WriteUART1(charArray). |
|||
== More Information == |
== More Information == |
||
The internal count of the encoder will "roll over" at 0 or 65535. It is up to you to note that if the encoder count has made an unreasonable change, it has probably rolled over! |
|||
NA |
|||
Latest revision as of 06:35, 16 January 2016
THIS PAGE REFERS TO A PRE-RELEASE VERSION OF THE NU32 PIC32 DEVELOPMENT BOARD. FOR INFORMATION, SAMPLE CODE, AND VIDEOS RELATED TO THE PRODUCTION VERSION (2016 AND LATER), AND TO THE CORRESPONDING BOOK "EMBEDDED COMPUTING AND MECHATRONICS WITH THE PIC32 MICROCONTROLLER," VISIT THE NU32 PAGE.
Using the dsPIC33FJ12MC201 breakout board for quadrature decoding.
Overview
Datasheet, Specifics on the QEI module
The dsPIC series of PIC microcontrollers are inexpensive 16 bit microcontrollers, specializing in the ability do fast digital signal processing.
The dsPIC33FJ12MC201 is a low pin count chip that runs on 3.3V at 80MHz without an external oscillator. It has the ability to remap peripheral functionality to any pins (labeled RPx). It also has a special peripheral called QEI, or Quadrature Encoder Interface. The QEI module receives the quadrature square waves from an encoder and keeps track of the net motion of the encoder as a 16 bit unsigned integer.
Details
The breakout board has been pre-programmed to read a quadrature signal on pins RP7 and RP8 (pins 11 and 12). It will keep track of the net motion of the encoder as a 16 bit integer, initializing to 32767. The dsPIC will report the 16 bit unsigned number over SPI communication when a '1' is sent.
Wiring
Library Functions
This code is an example of how to read the encoder count using the NU32.
The functions are:
- void initEncoderSPI(void) - enables SPI4 as master at 8MHz
- int getEncoder(void) - sends a '1' to the dsPIC, returns the value returned by the dsPIC
NU32_dsPIC_Example.c above demonstrates how to use the breakout board.
Sample Code
To initialize the SPI communication, call initEncoderSPI(), :
initEncoderSPI();
To read the encoder count, call getEncoder(), :
int count = getEncoder();
More Information
The internal count of the encoder will "roll over" at 0 or 65535. It is up to you to note that if the encoder count has made an unreasonable change, it has probably rolled over!