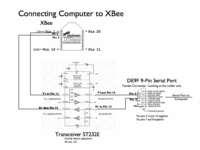
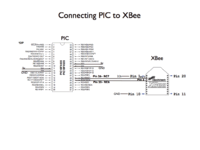
Difference between revisions of "ME 333 final projects"
EricNickel (talk | contribs) |
EricNickel (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
=== [[Programmable Stiffness Joint]] === |
=== [[Programmable Stiffness Joint]] === |
||
The purpose of this project is to develop a joint which can be externally programmed to take on a range of stiffnesses, as desired by the user. |
The purpose of this project is to develop a joint which can be externally programmed to take on a range of stiffnesses, as desired by the user. The strategy used in this application was to use a linear spring to provide stiffness and vary one moment arm distance via a sliding track, thereby adjusting the effective rotational stiffness of the joint. This device is a proof of concept device which demonstrates the feasibility of one strategy for designing an experimental unit for determining the respective roles of stiffness and damping in the human ankle. |
||
Future models should streamline the design of the device and add programmable damping elements which are independent of the stiffness elements, allowing researchers to alter the respective damping and stiffness values to mimic human gait kinematics, thereby determining the respective roles of damping and stiffness in able-bodied gait. This information would be valuable to the fields of biomechanics and prosthetics/orthotics. Research using such a device would advance knowledge in those fields and potentially enable the design of more intuitive and comfortable prostheses. |
|||
<br clear=all> |
<br clear=all> |
||
Revision as of 21:44, 9 March 2008
ME 333 Final Projects 2008
IR Tracker
The IR Tracker detects the position of an infrared emitter in two axises, and orients itself to line up with the emitter.
Project Title 2
Here are a few words describing your project, just a teaser to go with the picture at the side.
Learning Oscillator
The Learning Oscillator is given a desired acceleration profile for a linear oscillating mass. It then 'learns' and adjusts the frequency of its force source so the oscillating mass eventually matches the desired acceleration profile.
Programmable Stiffness Joint
The purpose of this project is to develop a joint which can be externally programmed to take on a range of stiffnesses, as desired by the user. The strategy used in this application was to use a linear spring to provide stiffness and vary one moment arm distance via a sliding track, thereby adjusting the effective rotational stiffness of the joint. This device is a proof of concept device which demonstrates the feasibility of one strategy for designing an experimental unit for determining the respective roles of stiffness and damping in the human ankle.
Future models should streamline the design of the device and add programmable damping elements which are independent of the stiffness elements, allowing researchers to alter the respective damping and stiffness values to mimic human gait kinematics, thereby determining the respective roles of damping and stiffness in able-bodied gait. This information would be valuable to the fields of biomechanics and prosthetics/orthotics. Research using such a device would advance knowledge in those fields and potentially enable the design of more intuitive and comfortable prostheses.