Difference between revisions of "Brushless DC Motors"
From Mech
Jump to navigationJump to search| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
===Commutation Circuitry=== |
===Commutation Circuitry=== |
||
Unlike a DC Motor which is automatically commutated by a Brushless DC Motor |
Unlike a DC Motor which is automatically commutated by a Brushless DC Motor |
||
[[File: |
[[File:Commutation.png]] |
||
==References== |
==References== |
||
Revision as of 09:37, 11 September 2013
Overview
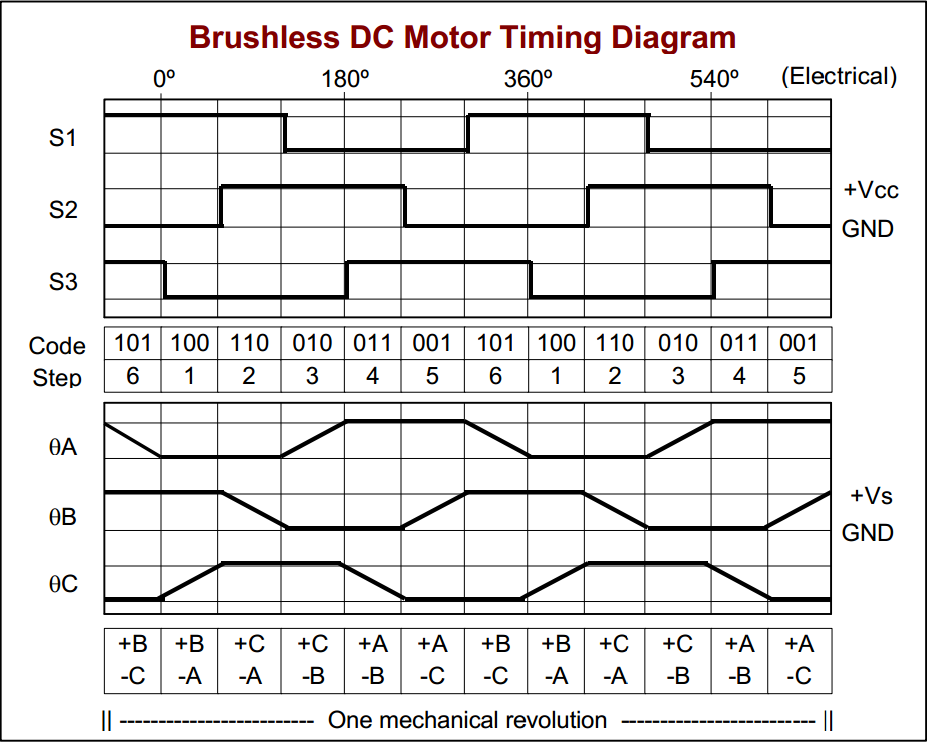
Brushless DC (BLDC) motors are similar to Brushed DC Motors, except the commutation is done electronically, and the permanent magnets are on the rotor and the coils on the stator. Instead of using the brushes and the rotation of the commutator to power the coils, external circuitry is used. Brushless DC motors are generally more expensive and the extra effort to construct the circuitry must be considered. However, BLDCs can be more efficient under light loads, typically have better power-to-weight ratios and produce less wear on internal components. BLDCs are used in computer hard drives, CD/DVD players, and PC cooling fans and electric cars.
Commutation Circuitry
Unlike a DC Motor which is automatically commutated by a Brushless DC Motor
References
- Wikipedia, "Brushless DC electric motor", http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brushless_motors