Difference between revisions of "PIC18F4520: Digital Inputs"
m |
m (→Sample Code) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Working with digital inputs and outputs is fundamental to circuit design, and PIC microcontrollers add versatility to design by allowing programming and re-programming of the logic associated with input and output pins. In this way, one PIC microcontroller can take the place of many pre-programmed digital logic ICs. |
|||
==Available Pins== |
==Available Pins== |
||
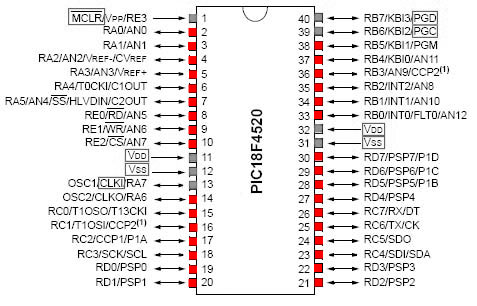
With the exception of the positive voltage supply and ground pins, all pins on the PIC18F4520 can be used as digital I/O, however a few other pins (shown in grey below) are commonly utilized for communication instead of digital I/O. |
With the exception of the positive voltage supply and ground pins, all pins on the PIC18F4520 can be used as digital I/O, however a few other pins (shown in grey below) are commonly utilized for communication instead of digital I/O. |
||
<br><br> |
|||
[[Image:4520pindiagramdigital.jpg|center]] |
|||
==Digital Inputs Example== |
|||
This section uses an example to describe how to set up and read digital inputs using a PIC18F4520. |
|||
===Sample Code=== |
|||
Program to display push-button input as LED output |
|||
First include header file with definitions for specific PIC. |
|||
Set fuses. HS is type of external clock, low voltage programming |
|||
(LVP) is off, and the watchdog timer (WDT) is off. |
|||
External clock frequency of 20 MHz is specified. |
|||
#include <18f4520.h> |
|||
#fuses HS,NOLVP,NOWDT |
|||
#use delay (clock=20000000) |
|||
Define pin names to be used in the main program. See header file |
|||
for currently defined pin names. |
|||
#define IN0 PIN_B0 |
|||
#define IN1 PIN_B1 |
|||
#define IN2 PIN_B2 |
|||
#define OUT0 PIN_D0 |
|||
#define OUT1 PIN_D1 |
|||
#define OUT2 PIN_D2 |
|||
Begin main body of program. |
|||
void main(void) { |
|||
Use while to set up infinite loop. |
|||
while(TRUE){ |
|||
Check each input pin and define action to be taken depending on |
|||
reading from input (in this case, set the output to the input). |
|||
if(input(IN0)) |
|||
output_high(OUT0); |
|||
else if (!input(IN0)) |
|||
output_low(OUT0); |
|||
if(input(IN1)) |
|||
output_high(OUT1); |
|||
else if (!input(IN1)) |
|||
output_low(OUT1); |
|||
if(input(IN2)) |
|||
output_high(OUT2); |
|||
else if (!input(IN2)) |
|||
output_low(OUT2);} |
|||
} |
|||
<br> |
|||
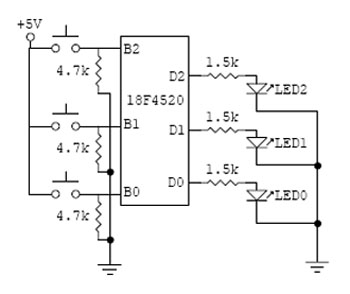
===Circuit Diagram=== |
|||
[[Image:Digitalinckt2.jpg]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 08:15, 5 July 2007
Working with digital inputs and outputs is fundamental to circuit design, and PIC microcontrollers add versatility to design by allowing programming and re-programming of the logic associated with input and output pins. In this way, one PIC microcontroller can take the place of many pre-programmed digital logic ICs.
Available Pins
With the exception of the positive voltage supply and ground pins, all pins on the PIC18F4520 can be used as digital I/O, however a few other pins (shown in grey below) are commonly utilized for communication instead of digital I/O.
Digital Inputs Example
This section uses an example to describe how to set up and read digital inputs using a PIC18F4520.
Sample Code
Program to display push-button input as LED output
First include header file with definitions for specific PIC. Set fuses. HS is type of external clock, low voltage programming (LVP) is off, and the watchdog timer (WDT) is off. External clock frequency of 20 MHz is specified.
#include <18f4520.h> #fuses HS,NOLVP,NOWDT #use delay (clock=20000000)
Define pin names to be used in the main program. See header file for currently defined pin names.
#define IN0 PIN_B0 #define IN1 PIN_B1 #define IN2 PIN_B2 #define OUT0 PIN_D0 #define OUT1 PIN_D1 #define OUT2 PIN_D2
Begin main body of program.
void main(void) {
Use while to set up infinite loop.
while(TRUE){
Check each input pin and define action to be taken depending on reading from input (in this case, set the output to the input).
if(input(IN0))
output_high(OUT0);
else if (!input(IN0))
output_low(OUT0);
if(input(IN1))
output_high(OUT1);
else if (!input(IN1))
output_low(OUT1);
if(input(IN2))
output_high(OUT2);
else if (!input(IN2))
output_low(OUT2);}
}