Difference between revisions of "PIC32MX: SPI External RAM"
(→Code) |
(→Code) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
This page will guide you how to interface the PIC32 board with the 23K256 external RAM using SPI. |
This page will guide you how to interface the PIC32 board with the 23K256 external RAM using SPI. |
||
The PIC32 communicates with the 23K256 through sending a series of 8 bit commands. To understand the 23K256 operations more thoroughly, consult the 23K256 datasheet. But basically, the PIC tells the 23K256 what mode to operate in, whether it is reading or writing, what address to use, and the data to store. |
|||
== Circuit == |
== Circuit == |
||
| Line 102: | Line 104: | ||
} |
} |
||
4. To see that the PIC32 and the external RAM are operating correctly, you can observe the communication lines. You should be able to see data, similar to that described in this microchip documentation http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/AppNotes/01277A.pdf]. |
4. To see that the PIC32 and the external RAM are operating correctly, you can observe the communication lines. You should be able to see data, similar to that described in this microchip documentation [http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/AppNotes/01277A.pdf]. |
||
5. You can also choose to view the data being sent and read through UART on the PC. You can do this by adding some code. First, |
5. You can also choose to view the data being sent and read through UART on the PC. You can also set up the LEDs on the PIC32 board to indicate whether the correct data is sent and received. You can do this by adding some code. First, add these two lines somewhere before the main loop: |
||
#define DESIRED_BAUDRATE (9600) // The desired BaudRate |
|||
void Delayms( unsigned t); |
|||
Then, configure UART2, adding this code to the start of the main loop: |
|||
mInitAllLEDs(); |
mInitAllLEDs(); |
||
| Line 127: | Line 134: | ||
putsUART2("Init Done\r\n"); |
putsUART2("Init Done\r\n"); |
||
//While loop to test LED functionality |
//While loop to test LED functionality |
||
Next, add this code to the bottom of the infinite while loop: |
|||
/************************************************************ |
|||
This "TESTER" section lets you view results via UART or test |
|||
accuracy of data transfer through the LEDS on the PIC32 board |
|||
************************************************************/ |
|||
//VIEW RESULTS THROUGH UART |
|||
//Byte Mode results |
|||
printf("\r\nBYTE MODE: "); |
|||
printf("BYTE MODE: Data Sent / Data Read = %d / %d\r\n", RandomSendData, ReadVal); |
|||
//Page Mode results |
|||
printf("\r\nPAGE MODE: "); |
|||
for(Cnt = 0;Cnt<32;Cnt++){ |
|||
printf("Data Sent / Data Read = %d / %d\r\n", SRAMBufPage[Cnt], SRAMBufCheckPage[Cnt]); |
|||
} |
|||
//Sequential Mode results |
|||
printf("\r\nSEQUENTIAL MODE: "); |
|||
for(Cnt = 0;Cnt<sizeof(SRAMBufSeq);Cnt++){ |
|||
printf("Data Sent / Data Read = %d / %d\r\n", SRAMBufSeq[Cnt], SRAMBufCheckSeq[Cnt]); |
|||
} |
|||
//TEST RESULTS THROUGH LEDS ON PIC32 BOARD. If data read not equal data sent, LED will be OFF |
|||
//Byte Mode results |
|||
if(ReadVal==RandomSendData){ |
|||
mLED_0_On(); |
|||
} |
|||
else{ |
|||
mLED_0_Off(); |
|||
} |
|||
//Page Mode results |
|||
for(Cnt = 0;Cnt<32;Cnt++){ |
|||
if(SRAMBufPage[Cnt]==SRAMBufCheckPage[Cnt]){ |
|||
mLED_1_On(); |
|||
} |
|||
else{ |
|||
mLED_1_Off(); |
|||
break; |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
//Sequential Mode results |
|||
for(Cnt = 0;Cnt<sizeof(SRAMBufSeq);Cnt++){ |
|||
if(SRAMBufSeq[Cnt]==SRAMBufCheckSeq[Cnt]){ |
|||
mLED_2_On(); |
|||
} |
|||
else{ |
|||
mLED_2_Off(); |
|||
break; |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
Delayms(1000); |
|||
/************************************************************ |
|||
...end of "TESTER" section. |
|||
************************************************************/ |
|||
Finally, add this to the very bottom of the main file: |
|||
void Delayms( unsigned t) |
|||
// This uses Timer 1, can be changed to another timer. Assumes FPB = SYS_FREQ |
|||
{ |
|||
OpenTimer1(T1_ON | T1_PS_1_256, 0xFFFF); |
|||
while (t--) |
|||
{ // t x 1ms loop |
|||
WriteTimer1(0); |
|||
while (ReadTimer1() < SYS_FREQ/256/1000); |
|||
} |
|||
CloseTimer1(); |
|||
} // Delayms |
|||
Latest revision as of 00:25, 16 February 2010
Original Assignment
Do not erase this section!
Your assignment is to interface to the SPI 23K256 SRAM chip.
Overview
This page will guide you how to interface the PIC32 board with the 23K256 external RAM using SPI.
The PIC32 communicates with the 23K256 through sending a series of 8 bit commands. To understand the 23K256 operations more thoroughly, consult the 23K256 datasheet. But basically, the PIC tells the 23K256 what mode to operate in, whether it is reading or writing, what address to use, and the data to store.
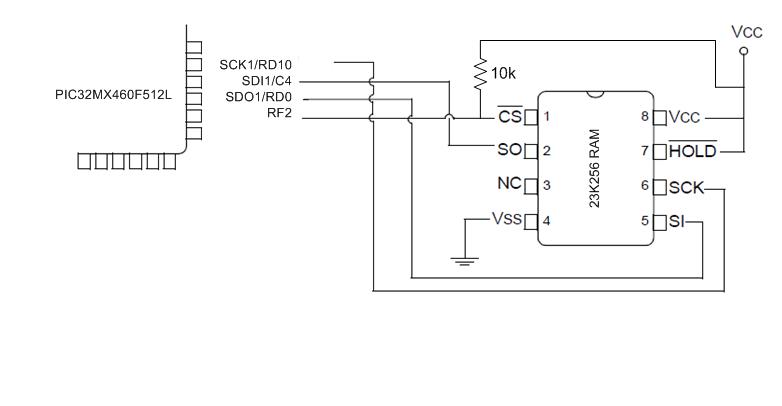
Circuit
Circuit diagram showing PIC32 connected to external RAM 23K256. The circuit is an edited version of a circuit from this microchip documentation [1].
Code
1. Go to this link [2] and download "AN1277 Source Code" folder.
2. Add the PIC32 files and other requirements to your MPLAB project; instructions here [3].
3. Edit the main.c file you downloaded from step 1 to match usage for the PIC32 board. The original code is also edited make testing easier. The code here has the PIC send data to store in the external RAM, and read the data back from the external RAM. It does this for the three modes available for the 23K256 external ram chip: byte mode, page mode, and sequential mode.
#include <plib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "HardwareProfile.h"
#include "SRAMDriver.h"
// Configuration Bit settings
// SYSCLK = 80 MHz (8MHz Crystal/ FPLLIDIV * FPLLMUL / FPLLODIV)
// PBCLK = 40 MHz
// Primary Osc w/PLL (XT+,HS+,EC+PLL)
// WDT OFF
// Other options are don't care
//
#pragma config FPLLMUL = MUL_20, FPLLIDIV = DIV_2, FPLLODIV = DIV_1, FWDTEN = OFF
#pragma config POSCMOD = HS, FNOSC = PRIPLL, FPBDIV = DIV_1
int main(void)
{
unsigned char ReadVal,Cnt;
unsigned char RandomSendData;
unsigned char SRAMBufPage[SRAMPageSize];
unsigned char SRAMBufCheckPage[SRAMPageSize];
unsigned char SRAMBufSeq[10];
unsigned char SRAMBufCheckSeq[10];
// Configure the device for maximum performance but do not change the PBDIV
// Given the options, this function will change the flash wait states, RAM
// wait state and enable prefetch cache but will not change the PBDIV.
// The PBDIV value is already set via the pragma FPBDIV option above..
SYSTEMConfig(SYS_FREQ, SYS_CFG_WAIT_STATES | SYS_CFG_PCACHE);
InitSRAM();
while(1)
{
//Byte Mode
SRAMWriteStatusReg(SRAMByteMode);
//Write random byte to 0x0010 memory location of SRAM
RandomSendData = rand();
SRAMWriteByte(0x00,0x10,RandomSendData);
//Read 0x0010 memory location of SRAM
ReadVal = SRAMReadByte(0x00,0x10);
//Page Mode
SRAMWriteStatusReg(SRAMPageMode);
memset(SRAMBufPage,0,sizeof(SRAMBufPage)); //Reset SRAMBuf location to 0x00 value
memset(SRAMBufCheckPage,0,sizeof(SRAMBufCheckPage)); //Reset SRAMBuf location to 0x00 value
//Write 32bytes from SRAMBuf array to first page of SRAM
for(Cnt = 0;Cnt<32;Cnt++)
{
SRAMBufPage[Cnt] = (rand());
}
SRAMWritePage(0x00,0x20,SRAMBufPage);
//Read 32bytes from SRAMBuf array from first page of SRAM
SRAMReadPage(0x00,0x20,SRAMBufCheckPage);
//Sequential Mode
memset(SRAMBufSeq,0,sizeof(SRAMBufSeq)); //Reset SRAMBuf location to 0x00 value
memset(SRAMBufCheckSeq,0,sizeof(SRAMBufCheckSeq)); //Reset SRAMBufCheckSeq location to 0x00 value
//Write 10bytes from SRAMBuf to SRAM starting from 0x0010 memory location
for(Cnt = 0;Cnt<32;Cnt++)
{
SRAMBufSeq[Cnt] =(rand());
}
SRAMWriteStatusReg(SRAMSeqMode);
SRAMWriteSeq(0x10,0x10,SRAMBufSeq,10);
//Read 10bytes starting from 0x1010 memory location of SRAM and store it to SRAMBuf array
SRAMReadSeq(0x10,0x10,SRAMBufCheckSeq,10);
}
}
4. To see that the PIC32 and the external RAM are operating correctly, you can observe the communication lines. You should be able to see data, similar to that described in this microchip documentation [4].
5. You can also choose to view the data being sent and read through UART on the PC. You can also set up the LEDs on the PIC32 board to indicate whether the correct data is sent and received. You can do this by adding some code. First, add these two lines somewhere before the main loop:
#define DESIRED_BAUDRATE (9600) // The desired BaudRate void Delayms( unsigned t);
Then, configure UART2, adding this code to the start of the main loop:
mInitAllLEDs();
int pbClk = SYSTEMConfigPerformance(SYS_FREQ);
#define config1 UART_EN | UART_IDLE_CON | UART_RX_TX | UART_DIS_WAKE | UART_DIS_LOOPBACK | UART_DIS_ABAUD | UART_NO_PAR_8BIT | UART_1STOPBIT | UART_IRDA_DIS | UART_DIS_BCLK_CTS_RTS| UART_NORMAL_RX | UART_BRGH_SIXTEEN
// define setup Configuration 2 for OpenUARTx
// IrDA encoded UxTX idle state is '0'
// Enable UxRX pin
// Enable UxTX pin
// Interrupt on transfer of every character to TSR
// Interrupt on every char received
// Disable 9-bit address detect
// Rx Buffer Over run status bit clear
#define config2 UART_TX_PIN_LOW | UART_RX_ENABLE | UART_TX_ENABLE | UART_INT_TX | UART_INT_RX_CHAR | UART_ADR_DETECT_DIS | UART_RX_OVERRUN_CLEAR
// Open UART2 with config1 and config2
OpenUART2( config1, config2, pbClk/16/DESIRED_BAUDRATE-1); // calculate actual BAUD generate value.
//OpenUART2( UART_EN | UART_NO_PAR_8BIT | UART_1STOPBIT, UART_RX_ENABLE | UART_TX_ENABLE, (pbClk/16/DESIRED_BAUDRATE
putsUART2("Init Done\r\n");
//While loop to test LED functionality
Next, add this code to the bottom of the infinite while loop:
/************************************************************
This "TESTER" section lets you view results via UART or test
accuracy of data transfer through the LEDS on the PIC32 board
************************************************************/
//VIEW RESULTS THROUGH UART
//Byte Mode results
printf("\r\nBYTE MODE: ");
printf("BYTE MODE: Data Sent / Data Read = %d / %d\r\n", RandomSendData, ReadVal);
//Page Mode results
printf("\r\nPAGE MODE: ");
for(Cnt = 0;Cnt<32;Cnt++){
printf("Data Sent / Data Read = %d / %d\r\n", SRAMBufPage[Cnt], SRAMBufCheckPage[Cnt]);
}
//Sequential Mode results
printf("\r\nSEQUENTIAL MODE: ");
for(Cnt = 0;Cnt<sizeof(SRAMBufSeq);Cnt++){
printf("Data Sent / Data Read = %d / %d\r\n", SRAMBufSeq[Cnt], SRAMBufCheckSeq[Cnt]);
}
//TEST RESULTS THROUGH LEDS ON PIC32 BOARD. If data read not equal data sent, LED will be OFF
//Byte Mode results
if(ReadVal==RandomSendData){
mLED_0_On();
}
else{
mLED_0_Off();
}
//Page Mode results
for(Cnt = 0;Cnt<32;Cnt++){
if(SRAMBufPage[Cnt]==SRAMBufCheckPage[Cnt]){
mLED_1_On();
}
else{
mLED_1_Off();
break;
}
}
//Sequential Mode results
for(Cnt = 0;Cnt<sizeof(SRAMBufSeq);Cnt++){
if(SRAMBufSeq[Cnt]==SRAMBufCheckSeq[Cnt]){
mLED_2_On();
}
else{
mLED_2_Off();
break;
}
}
Delayms(1000);
/************************************************************
...end of "TESTER" section.
************************************************************/
Finally, add this to the very bottom of the main file:
void Delayms( unsigned t)
// This uses Timer 1, can be changed to another timer. Assumes FPB = SYS_FREQ
{
OpenTimer1(T1_ON | T1_PS_1_256, 0xFFFF);
while (t--)
{ // t x 1ms loop
WriteTimer1(0);
while (ReadTimer1() < SYS_FREQ/256/1000);
}
CloseTimer1();
} // Delayms