Difference between revisions of "PIC32MX: Interfacing with Force Sensors from a Scale"
JoshuaPeng (talk | contribs) (→Code) |
NickMarchuk (talk | contribs) |
||
| (106 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== |
== Overview == |
||
A BME Senior Design project group is developing a device to measure the weight shifting ability of a child with Cerebral Palsy. The end goal is to develop a video game that is controlled by the child shifting their weight. Hopefully this device will allow the children to improve their balance while having fun playing a video game. |
|||
'''Do not erase this section!''' |
|||
Our portion of the project involves designing the hardware to read the signals from 4 load cells and writing code to read in the load values to a PIC 32 microcontroller which is then sent to a PC via RS232. Additionally we developed an interface for the PC that visually represents the collected data in a useful and intuitive format. |
|||
Your assignment is to use four analog inputs to continuously read four force sensors taken from a bathroom scale, and to display them on a PC screen as bars whose length corresponds to the force at the sensors. You will use Processing for the PC data acquisition and graphics. |
|||
== Overview == |
|||
[[Image:LAB5_Force_Sense_Block_Diagram.png]] |
|||
Summarize briefly what the page is about. |
|||
== Circuit == |
== Circuit == |
||
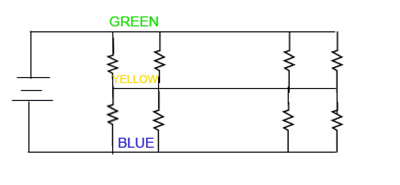
Each load sensor acts as a half bridge rectifier. When a potential difference is applied across the bridge, changes in load can be measured by sensing the voltage change at the middle of the bridge. This voltage change will be on the order of a few microvolts for most load cells. |
|||
Include a schematic and give any part numbers. A photo of your circuit is OK, but not as a replacement for a schematic. |
|||
[[Image:Scale_picture.jpg | 200px]] [[Image:LAB5_Force_Sense_Load_Cell.png]] |
|||
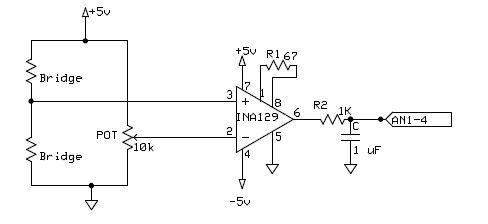
In order to read this very small change in voltage you need to use an [[http://www.mech.northwestern.edu/courses/433/Writeups/InstAmp/instamp.htm Instrumentation Amplifier]]. Instrumentation amplifiers read in two voltages and multiply the difference by a value specified by an external gain resistor. |
|||
== Code == |
|||
To complete the second half of the Wheatstone bridge a potentiometer is used. This potentiometer can be tuned to match the voltage produced by the load cell when no weight is applied. Therefore as more weight is applied the voltage out of the amplifier will increase until saturation of the amp is reached. This tunning is very important and can be time consuming because an initial offset of a few millivolts can force the amplifier to saturation. |
|||
Where possible, make it a single piece of well-commented cut-and-pastable code, or at least make each function that way, so others can easily copy it. Most comments should be in the code itself; outside the code (on the wiki) should only be explanatory comments that are too cumbersome to include in the code. |
|||
[[Image:LAB5_Force_Sense_Circut.png]] [[Image:Circut_picture.jpg | 200px]] |
|||
The signal that leaves the amp is fairly noisy so a low pass filter is used to smooth out the signal that is sent to the ADC. |
|||
== PIC Code == |
|||
The purpose of this code is to take the input signals (amplified voltage differences) from the 4 individual force sensors on the scale and output a string of 4 floats separated by spaces ending with a new line. This string will be sent out using RS232 and deciphered by Processing. |
|||
'''The Processing portion of our lab involves 4 main sections, these are the parts that are actually displayed in the Processing window:''' |
|||
'''ADC:''' |
|||
''1. Colorbars [colorbars();]:'' |
|||
In order to use the Analog-to-Digital converter embedded in PIC, we used Nick’s example, [http://hades.mech.northwestern.edu/index.php/PIC32MX:_Analog_Inputs PIC32MX: Analog Input]. Copy all the lines in this link except for the infinite while loop. However, you want to have four analog inputs for this project therefore you will need to change the number of analog inputs since this example only uses two analog inputs. |
|||
Do the following modifications in order to have four analog inputs. |
|||
#define PARAM2, you need four samples, so change ADC_SAMPLES_PER_INT_2 --> ADC_SAMPLES_PER_INT_4. |
|||
#define PARAM4, you also need to enable AN3 and AN4 as well with AN1 and AN2, |
|||
#define PARAM5, you don’t want to skip AN3 and AN4, so remove these two inputs from this parameter. |
|||
'''Interrupt Handler:''' |
|||
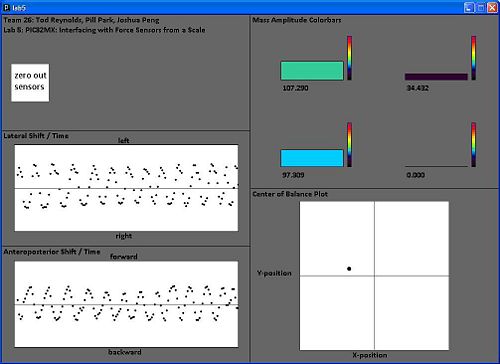
continuously displaying the force applied onto each force sensor by using 4 bars that will grow or shrink depending on the amplitude of mass (force). The bars will also show the amplitude of the mass by changing colors. When 0 or little force is applied, then corresponding bar is black colored, at the max force, the bar is orchid (pink) colored. |
|||
This function will affect our code only if the PIC receives a data from the processing via RS232 cable. If the interrupt occurs, it will first check whether the receive input interrupt flag was generated or transmit output interrupt flag was generated. And if it was the receive input interrupt, then it will save the value it received to the volatile unsigned char data, which we declared as a global variable. Then, the next line of code is a switch statement. |
|||
If it reads the character 'p' from volatile unsigned char data, which is sent from Processing when the 'zero out sensors' button is pressed, then it will record the initial values of the four sensors. |
|||
''2. XY-Plot [xyplot();]:'' |
|||
The full code can be found [http://hades.mech.northwestern.edu/images/9/9b/PIC_scale_convert.zip here]. |
|||
continuously displays the x- and y- position of the center of balance calculated between all 4 sensors with a dot on a xy-coordinate plane. So, if the person shifts his weight to the right side of scale, then the dot will move to the right in the x direction. If the person shifts his weight to the front of the sensor, then the dot will move up in the y direction. |
|||
''3. X-position vs. Time (not a separate function):'' |
|||
'''"main.c"''' |
|||
continuously plots a dot for the x-position along a time axis. This plot will be useful to see how much the person shifts his/her weight to the left or right (sagittal plane) over time. Due to the window size and the speed of processing, the points will be plotted over a time period of about 20 seconds. |
|||
''4. Y-position vs. time (not a separate function):'' |
|||
Main Function |
|||
continuously plots a dot for the y-position along a time axis. This plot will be useful to see how much the person shifts his/her weight forward or backwards (coronal or frontal plane) over time. The code for this section is essentially the same as the x-position but edited to show y-position. |
|||
<pre> |
|||
int main(void) |
|||
{ |
|||
int pbClk; |
|||
// Sets the B port to Analog Input |
|||
AD1PCFG = 0xFFFF; |
|||
// Configure the proper PB frequency and the number of wait states |
|||
pbClk = SYSTEMConfigPerformance(SYS_FREQ); |
|||
// Allow vector interrupts |
|||
INTEnableSystemMultiVectoredInt(); |
|||
mInitAllLEDs(); |
|||
initUART2(pbClk); |
|||
initADC(); |
|||
while(1) |
|||
{ |
|||
// read each sensor, subtract zero state value, |
|||
top_left= ReadADC10(0)-top_left_initial; |
|||
top_right= ReadADC10(1)-top_right_initial; |
|||
bottom_left= ReadADC10(2)-bottom_left_initial; |
|||
bottom_right= ReadADC10(3)-bottom_right_initial; |
|||
//Send to PC via RS232 |
|||
sendDataRS232(); |
|||
} |
|||
} //end main |
|||
'''Additional Functions in our Processing Code that are not displayed in the Processing window but are important:''' |
|||
</pre> |
|||
== Processing Code == |
|||
''1. Communication between the PC (Processing) and the PIC via RS232 [void initSerial();]'' |
|||
'''The Processing portion of our lab involves 4 visible sections:''' |
|||
The purpose of InitSerial(); is to open a serial port on the PC and communicate with the PIC32. The code found here is essentially a modification of the ME333 Lab 4: Motor Control Processing code written by Nick Marchuk. |
|||
1. Colorbars, ''colorbars();'' |
|||
continuously displaying the force applied onto each force sensor by using 4 bars that will grow or shrink depending on the amplitude of mass (force). The bars will also show the amplitude of the mass by changing colors. When 0 or little force is applied, then corresponding bar is black colored, at the max force, the bar is orchid (pink) colored. |
|||
Calculates the x-position based on the contribution of each force sensor output and returns the resulting float value. |
|||
2. XY-Plot, ''xyplot();'' |
|||
Calculates the y-position based on the contribution of each force sensor output and returns the resulting float value. |
|||
continuously displays the x- and y- position of the center of balance calculated between all 4 sensors with a dot on a xy-coordinate plane. So, if the person shifts his weight to the right side of scale, then the dot will move to the right in the x direction. If the person shifts his weight to the front of the sensor, then the dot will move up in the y direction. The corners represent one sensor at it's maximum amplitude (of 255) with the rest of the sensors at zero amplitude. |
|||
3. X-position vs. Time ''(not a separate function)'' |
|||
General Notes: |
|||
continuously plots a dot for the x-position along a time axis. This plot will be useful to see how much the person shifts his/her weight to the left or right (lateral shift) over time. Due to the window size and the speed of processing, the points will be plotted over a time period of about 20 seconds. |
|||
Our code was written with the assumption that the inputs from the PIC (that initially comes from the 4 force sensors) will come in the form of a 4x1 array. It does not actually arrive in that form from the PIC, it actually arrives as a string of floats separated by spaces ending with a new line. The new line is deleted and the floats are extracted out, normalized between 0-255, and put into the "mass" array. All of the normalization, window dimension parameters, rectangle dimensions, etc. were set up with the 0-255 range and 1000x700 window size in mind. So if the values are not between 0-255 or the window size is altered, almost all of following code will be messed up. The x-position vs. time and y-position vs. time plots are not implemented as independent functions. The code for these plots are found at the very end of colorbars();. |
|||
4. Y-position vs. time ''(not a separate function)'' |
|||
continuously plots a dot for the y-position along a time axis. This plot will be useful to see how much the person shifts his/her weight forward or backwards (anteroposterior shift) over time. The code for this section is essentially the same as the x-position but edited to show y-position. |
|||
Global Variables |
|||
<pre> |
|||
//initialization of the serial variable that will hold the values sent from the PIC via RS232 |
|||
import processing.serial.*; |
|||
Serial[] myPorts = new Serial[1]; |
|||
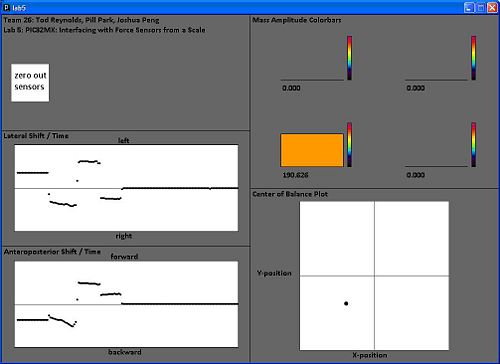
'''Screenshots:''' exerting force on the sensors in a circular pattern (left) and exerting force on one sensor at a time (right). |
|||
//the PIC will output 4 floats and we will first store the values into these 4 variables |
|||
float input0; |
|||
float input1; |
|||
float input2; |
|||
float input3; |
|||
[[Image:Circle.jpg | 500px]] [[Image:loadon1sensor.jpg | 500px]] |
|||
//dimensions of our window will be 1000x700 |
|||
float window_height = 700; |
|||
float window_width = 1000; |
|||
PFont fontA; //initializing our text font |
|||
//the main "mass" 4x1 array that holds the values continuously sent from the 4 force sensors |
|||
//we will refer to this array as the "mass array" in our comments |
|||
float[] mass = new float[4]; |
|||
'''Other Important Functions:''' |
|||
//window dimension variable that is used to make the bargraph. The bx and by variables are |
|||
//used so that the bargraph section could be more easily formatted in case we change the |
|||
//window size. |
|||
float bx = window_width/2/8; |
|||
float by = window_height/2/8; |
|||
int index; |
|||
1. Communication between the PC (Processing) and the PIC via RS232, ''void initSerial();'' |
|||
//color variables used to indicate the amplitude of the force applied to each sensor |
|||
color c0; |
|||
color c1; |
|||
color c2; |
|||
color c3; |
|||
</pre> |
|||
The purpose of InitSerial(); is to open a serial port on the PC and communicate with the PIC32. The code found here is essentially a modification of the ME333 Lab 4: Motor Control Processing code written by Nick Marchuk. |
|||
Main Setup Function |
|||
<pre> |
|||
void setup() { |
|||
index = 0; |
|||
InitSerial(); |
|||
smooth(); |
|||
2. X-position, ''float xposition();'' |
|||
//splitting the window into 5 separate areas and filling them with a 102 gray color |
|||
size(int(window_width),int(window_height)); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect(0,0,window_width/2,window_height/3); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect(0,window_height/3,window_width/2,window_height/3); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect(0,window_height*2/3,window_width/2,window_height/3); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect(window_width/2,0,window_width/2,window_height/2); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect(window_width/2,window_height/2,window_width/2,window_height/2); |
|||
Calculates the x-position based on the contribution of each force sensor output and returns the resulting float value. |
|||
//filling inside of the x-position vs. time and y-position vs. time plots with white color |
|||
fill(255); |
|||
rect(25, int(window_height/3)+29, int(window_width/2)-49, int(window_height/3)-59); |
|||
fill(255); |
|||
rect(25, int(window_height*2/3)+29, int(window_width/2)-49, int(window_height/3)-59); |
|||
} |
|||
</pre> |
|||
3. Y-position, ''float yposition();'' |
|||
Main Draw Function |
|||
<pre> |
|||
void draw() { |
|||
//when we first tried to see if each of the 4 parts in our code worked, we assigned the mass array to pick |
|||
//up the cursor position in the window. |
|||
/* |
|||
mass[0] = ((1000-mouseX)/7.84314)+((700-mouseY)/5.4902); |
|||
mass[1] = (mouseX/7.84314)+((700-mouseY)/5.4902); |
|||
mass[2] = ((1000-mouseX)/7.84314)+(mouseY/5.4902); |
|||
mass[3] = (mouseX/7.84314)+(mouseY/5.4902); |
|||
*/ |
|||
Calculates the y-position based on the contribution of each force sensor output and returns the resulting float value. |
|||
//initializing font we want to use |
|||
fontA = loadFont("Calibri-Bold-16.vlw"); |
|||
4. Button to zero out force sensors |
|||
textFont(fontA); |
|||
/*calling our xy-plot and colorbars functions. The x-position vs. time and y-position vs. time plots |
|||
are not actually separate functions. They are a short section of code found at the very end of the |
|||
colorbars function. In order to make the x-position vs. time and y-position vs. time plots work we |
|||
needed variables found only in colorbars. |
|||
*/ |
|||
xyplot(); |
|||
colorbars(); |
|||
} |
|||
</pre> |
|||
Adds a button to zero out the force sensors. Noise displaces our dot in the xy-plot from the center when we first turn on our circuit. There is an interrupt function in the main.c file that will do the "zeroing out" and output altered values once this button is pressed. The code for this button was taken from ME333 Lab 4: Motor Control, written by Nick Marchuk. |
|||
Communication between the PC (Processing) and the PIC via RS232 |
|||
<pre> |
|||
void InitSerial() { |
|||
// initialize the serial port |
|||
// List all the available serial ports |
|||
// you want the one that you plugged in |
|||
println(Serial.list()); |
|||
String portList = Serial.list()[0]; |
|||
// this assumes the COM port you want is the first one, change the 0 to the place of your comport in the list that appears in the debug window |
|||
myPorts[0] = new Serial(this, portList, 19200); |
|||
'''Notes on relative amplitude range and mapping:''' |
|||
// read bytes into a buffer until you get a linefeed (ASCII 10): |
|||
myPorts[0].bufferUntil('\n'); |
|||
} |
|||
Our code was written with the assumption that the inputs from the PIC (that initially comes from the 4 force sensors) will come in the form of a 4x1 array. It does not actually arrive in that form from the PIC, it actually arrives as a string of floats separated by spaces ending with a new line. The new line is deleted and the floats are extracted out, normalized between 0-255, and put into the "mass" array. All of the normalization, window dimension parameters, rectangle dimensions, etc. were set up with the 0-255 range and 1000x700 window size in mind. So if the values are not between 0-255 or the window size is altered, almost all of following code will be messed up. The x-position vs. time and y-position vs. time plots are not implemented as independent functions. The code for these plots are found at the very end of colorbars();. |
|||
// serial event, check which port generated the event, just in case there are more than 1 ports open |
|||
void serialEvent(Serial thisPort) { |
|||
// variable to hold the number of the port: |
|||
int portNumber = -1; |
|||
One of the global variables, mapping integer "m," determines the sensitivity of the sensors. Our potentiometers are tuned to output a miniscule positive voltage difference which is amplified by 675. The resulting value falls within our initial range of 0-m (default: 0-511) which is then mapped to a floating-point number range 0-255. We found that the default initial range of 0-511 (m = 511) works well for adults standing on the scale. For adults using their hands to exert force on the scale, the range 0-200 (m = 200) is more suitable. Thus, as m is decreased, the sensitivity is increased. This mapping variable can be altered for each individual user, especially cerebral palsy patients, for which this scale is designed. |
|||
// iterate over the list of ports opened, and match the |
|||
// one that generated this event: |
|||
for (int p = 0; p < myPorts.length; p++) { |
|||
if (thisPort == myPorts[p]) { |
|||
portNumber = p; |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
==Next Steps== |
|||
// read the serial buffer until a newline appears |
|||
String myString = thisPort.readStringUntil('\n'); |
|||
// if you got any bytes other than the newline |
|||
if (myString != null) { |
|||
myString = trim(myString); // ditch the newline |
|||
1. Develop a printed circuit board that contains all amplification circuitry, the microcontroller, and tunning circuits. Additionally, redesign the tunning circuit so that it is more robust. |
|||
// split the string at the spaces, save as integers |
|||
float line_received[] = float(split(myString, ' ')); |
|||
2. Find a formula(hopefully linear) that equates the voltages seen from the sensors to mass. This can be done by using a few objects whose mass's are known. |
|||
// grab the data |
|||
if ((line_received.length == 4) && (portNumber==0)){ |
|||
if (index >= 4){ |
|||
index = 0; |
|||
} |
|||
/*setting the ranges for the values received to be between 0-255, then |
|||
putting those values into our mass array |
|||
3. Develop a chart that details what the "m" mapping variable value should be for a user's body weight and configure the scale to automatically adjust the m value when a user steps on the scale. |
|||
Right now, we are using a intermediate variable (inputx) to carry |
|||
the value to the mass array just incase we need a variable to edit |
|||
without having to edit the mass array values. |
|||
*/ |
|||
input0 = map(line_received[0],-1000,1000,510,0); |
|||
input1 = map(line_received[1],-1000,1000,510,0); |
|||
input2 = map(line_received[2],-1000,1000,510,0); |
|||
input3 = map(line_received[3],-1000,1000,510,0); |
|||
if (input0 < 0) { |
|||
mass[0] = 0; |
|||
} |
|||
else if (input0 >= 0) { |
|||
mass[0] = input0; |
|||
} |
|||
if (input1 < 0) { |
|||
mass[1] = 0; |
|||
} |
|||
else if (input1 >= 0) { |
|||
mass[1] = input1; |
|||
} |
|||
if (input2 < 0) { |
|||
mass[2] = 0; |
|||
} |
|||
else if (input2 >= 0) { |
|||
mass[2] = input2; |
|||
} |
|||
if (input3 < 0) { |
|||
mass[3] = 0; |
|||
} |
|||
else if (input3 >= 0) { |
|||
mass[3] = input3; |
|||
} |
|||
index++; |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
} // end serialEvent |
|||
</pre> |
|||
4. Also, make the colorbars or plot dots change to a certain color and/or have the computer play a sound when a certain mass amplitude value on a sensor has been breached. This may be useful for cerebral palsy patients that are being trained to maintain balance. |
|||
XY-Plot |
|||
<pre> |
|||
void xyplot(){ |
|||
//setting xy-plot window dimensions, plotting x-axis and y-axis lines, and plotting the actual point that |
|||
//moves around in the xy-coordinate plane |
|||
float sizeofwindow = window_width/2-2*window_width/10; |
|||
float j = 510; |
|||
fill(255); |
|||
strokeWeight(1); |
|||
rect(window_width/2+window_width/10,window_height/2+window_height/28,sizeofwindow,sizeofwindow); |
|||
strokeWeight(1); |
|||
stroke(75); |
|||
line(.75*window_width, window_height/2+window_height/28, .75*window_width, window_height-window_height/28); |
|||
line(window_width/2+window_width/10, .75*window_height, window_width-window_width/10, .75*window_height); |
|||
float x = (sizeofwindow/j)*xposition(); |
|||
float y = (sizeofwindow/j)*yposition(); |
|||
stroke(c3); |
|||
fill(0); |
|||
strokeWeight(5); |
|||
point(x+window_width*3/4,y+window_height*3/4); |
|||
strokeWeight(1); |
|||
//displaying text and titles, note that titles may be different than just "colorbars" and "xy-plot," |
|||
//but they are the same thing. |
|||
fill(0); |
|||
text("Team 26: Tod Reynolds, Pill Park, Joshua Peng", 4, 16); |
|||
text("Lab 5: PIC32MX: Interfacing with Force Sensors from a Scale", 4, 36); |
|||
text("Mass Amplitude Colorbars", window_width/2+5, 16); |
|||
text("Center of Balance Plot", window_width/2+5, window_height/2+16); |
|||
text("X-position", window_width*3/4-window_width/23,window_height-10); |
|||
text("Y-position", window_width/2+15, window_height*3/4); |
|||
text("Sagittal Shift / Time", 5, window_height/3+16); |
|||
text("Coronal Shift / Time", 5, window_height*2/3+16); |
|||
text("left", (window_width/4)-15, window_height/3+26); |
|||
text("forward", (window_width/4)-30, window_height*2/3+26); |
|||
text("right", (window_width/4)-20, window_height*2/3-16); |
|||
text("backward", (window_width/4)-35, window_height-16); |
|||
} |
|||
</pre> |
|||
X-position |
|||
<pre> |
|||
float xposition(){ |
|||
==Files== |
|||
//xposition(); returns a float value that specifies the x-position for the |
|||
//xy-plot, x-position vs. time, and y-position vs. time plots |
|||
float L; |
|||
float R; |
|||
float Xpos; |
|||
L = (mass[0]+mass[2])/2; |
|||
R = (mass[1]+mass[3])/2; |
|||
Xpos = R-L; |
|||
return Xpos; |
|||
} |
|||
</pre> |
|||
The full Processing code can be found [http://hades.mech.northwestern.edu/images/5/54/Processing_lab5.zip here]. |
|||
Y-position |
|||
<pre> |
|||
float yposition(){ |
|||
A full zip file containing the PIC code, Processing code, images, screenshots can be found [http://hades.mech.northwestern.edu/images/c/c7/Lab5-021110.zip here]. |
|||
//yposition(); returns a float value that specifies the y-position for the |
|||
//xy-plot, x-position vs. time, and y-position vs. time plots |
|||
float T; |
|||
float B; |
|||
float Ypos; |
|||
T = (mass[0]+mass[1])/2; |
|||
B = (mass[2]+mass[3])/2; |
|||
Ypos = B-T; |
|||
return Ypos; |
|||
} |
|||
</pre> |
|||
A link to a demonstration video of the force sensing scale can be found [http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fIQMORTUFRo here]. |
|||
Colorbars |
|||
<pre> |
|||
void colorbars() |
|||
{ |
|||
float x = window_width/2; |
|||
float y = 0; |
|||
//initializing lots of variables to hold values for the mass array, rectangle positions, and color |
|||
float s0 = mass[0]; |
|||
float s1 = mass[1]; |
|||
float s2 = mass[2]; |
|||
float s3 = mass[3]; |
|||
color r0; |
|||
color r1; |
|||
color r2; |
|||
color r3; |
|||
//the 9 colors with rgb values that we will transition through as the mass amplitude increases |
|||
color black = color(0, 0, 0); |
|||
color plum = color(68, 0, 51); |
|||
color navy = color(0, 0, 128); |
|||
color sky = color(0, 191, 255); |
|||
color lime = color(127, 255, 0); |
|||
color sun = color(255, 255, 0); |
|||
color fire = color(250, 140, 0); |
|||
color tomato = color(255, 0, 0); |
|||
color orchid = color(199, 21, 133); |
|||
//text labels incase we want to label the mass amplitude values |
|||
/* |
|||
String str0 = "Left Top Sensor Mass: "; |
|||
String str1 = "Right Top Sensor Mass: "; |
|||
String str2 = "Left Bottom Sensor Mass: "; |
|||
String str3 = "Right Bottom Sensor Mass: "; |
|||
*/ |
|||
/*the next section of code creates color intervals and the colorbars. Since we are assuming |
|||
that each of the 4 floats in the mass array will be values between 0-255, we created 8 intervals |
|||
for color interpolation. Each interval is 32 points long, so in total we will have 256 points |
|||
(8x32 = 256). |
|||
The 8 intervals are: |
|||
black to plum (0-31) |
|||
plum to navy (32-63) |
|||
navy to sky (64-95) |
|||
sky to lime (96-127) |
|||
lime to sun (128-159) |
|||
sun to fire (160-191) |
|||
fire to tomato (192-223) |
|||
tomato to orchid (224-255) |
|||
Colorbars are rectangles with a width of (window_width/4) and a height varying according to the mass amplitude. |
|||
The max height is (window_height/4). Since the PIC is continuously sending different values in, this section of |
|||
code (that is called in draw();) is run over and over again, as if in a infinite loop. The general algorithm for |
|||
the colorbars is first to "erase" the last rectangle by plotting a rectangle filled with the background color |
|||
and with no stroke, and then to plot a new rectangle on top. This "erasing" is so that you do not see the last rectangle |
|||
behind the current rectangle. |
|||
*/ |
|||
//sensor0 colorbars |
|||
//please note that this next section of code is basically repeated 3 more times to create 3 more bars |
|||
if (s0 <= 31) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+bx), 40, bx*2.1, by*3); |
|||
c0 = lerpColor(black, plum, s0/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c0); |
|||
rect((x+bx), (3*by)-(2*by)*(mass[0]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[0]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s0 <= 63) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+bx), 40, bx*2.1, by*3); |
|||
c0 = lerpColor(plum, navy, (s0-32)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c0); |
|||
rect((x+bx), (3*by)-(2*by)*(mass[0]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[0]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s0 <= 95) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+bx), 40, bx*2.1, by*3); |
|||
c0 = lerpColor(navy, sky, (s0-63)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c0); |
|||
rect((x+bx), (3*by)-(2*by)*(mass[0]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[0]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s0 <= 127) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+bx), 40, bx*2.1, by*3); |
|||
c0 = lerpColor(sky, lime, (s0-95)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c0); |
|||
rect((x+bx), (3*by)-(2*by)*(mass[0]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[0]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s0 <= 159) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+bx), 40, bx*2.1, by*3); |
|||
c0 = lerpColor(lime, sun, (s0-127)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c0); |
|||
rect((x+bx), (3*by)-(2*by)*(mass[0]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[0]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s0 <= 191) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+bx), 40, bx*2.1, by*3); |
|||
c0 = lerpColor(sun, fire, (s0-159)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c0); |
|||
rect((x+bx), (3*by)-(2*by)*(mass[0]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[0]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s0 <= 223) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+bx), 40, bx*2.1, by*3); |
|||
c0 = lerpColor(fire, tomato, (s0-191)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c0); |
|||
rect((x+bx), (3*by)-(2*by)*(mass[0]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[0]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s0 <= 255) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+bx), 40, bx*2.1, by*3); |
|||
c0 = lerpColor(tomato, orchid, (s0-223)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c0); |
|||
rect((x+bx), (3*by)-(2*by)*(mass[0]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[0]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
//sensor1 colorbars |
|||
if (s1 <= 31) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), 40, bx*2.1, by*3); |
|||
c1 = lerpColor(black, plum, s1/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c1); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), (3*by)-(2*by)*(mass[1]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[1]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s1 <= 63) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), 40, bx*2.1, by*3); |
|||
c1 = lerpColor(plum, navy, (s1-32)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c1); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), (3*by)-(2*by)*(mass[1]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[1]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s1 <= 95) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), 40, bx*2.1, by*3); |
|||
c1 = lerpColor(navy, sky, (s1-63)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c1); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), (3*by)-(2*by)*(mass[1]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[1]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s1 <= 127) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), 40, bx*2.1, by*3); |
|||
c1 = lerpColor(sky, lime, (s1-95)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c1); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), (3*by)-(2*by)*(mass[1]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[1]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s1 <= 159) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), 40, bx*2.1, by*3); |
|||
c1 = lerpColor(lime, sun, (s1-127)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c1); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), (3*by)-(2*by)*(mass[1]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[1]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s1 <= 191) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), 40, bx*2.1, by*3); |
|||
c1 = lerpColor(sun, fire, (s1-159)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c1); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), (3*by)-(2*by)*(mass[1]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[1]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s1 <= 223) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), 40, bx*2.1, by*3); |
|||
c1 = lerpColor(fire, tomato, (s1-191)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c1); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), (3*by)-(2*by)*(mass[1]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[1]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s1 <= 255) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), 40, bx*2.1, by*3); |
|||
c1 = lerpColor(tomato, orchid, (s1-223)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c1); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), (3*by)-(2*by)*(mass[1]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[1]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
//sensor2 colorbars |
|||
if (s2 <= 31) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+bx), 4*by, bx*2.1, 3*by); |
|||
c2 = lerpColor(black, plum, s2/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c2); |
|||
rect((x+bx), (7*by)-(2*by)*(mass[2]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[2]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s2 <= 63) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+bx), 4*by, bx*2.1, 3*by); |
|||
c2 = lerpColor(plum, navy, (s2-32)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c2); |
|||
rect((x+bx), (7*by)-(2*by)*(mass[2]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[2]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s2 <= 95) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+bx), 4*by, bx*2.1, 3*by); |
|||
c2 = lerpColor(navy, sky, (s2-63)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c2); |
|||
rect((x+bx), (7*by)-(2*by)*(mass[2]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[2]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s2 <= 127) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+bx), 4*by, bx*2.1, 3*by); |
|||
c2 = lerpColor(sky, lime, (s2-95)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c2); |
|||
rect((x+bx), (7*by)-(2*by)*(mass[2]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[2]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s2 <= 159) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+bx), 4*by, bx*2.1, 3*by); |
|||
c2 = lerpColor(lime, sun, (s2-127)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c2); |
|||
rect((x+bx), (7*by)-(2*by)*(mass[2]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[2]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s2 <= 191) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+bx), 4*by, bx*2.1, 3*by); |
|||
c2 = lerpColor(sun, fire, (s2-159)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c2); |
|||
rect((x+bx), (7*by)-(2*by)*(mass[2]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[2]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s2 <= 223) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+bx), 4*by, bx*2.1, 3*by); |
|||
c2 = lerpColor(fire, tomato, (s2-191)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c2); |
|||
rect((x+bx), (7*by)-(2*by)*(mass[2]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[2]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s2 <= 255) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+bx), 4*by, bx*2.1, 3*by); |
|||
c2 = lerpColor(tomato, orchid, (s2-223)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c2); |
|||
rect((x+bx), (7*by)-(2*by)*(mass[2]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[2]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
//sensor3 colorbars |
|||
if (s3 <= 31) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), 4*by, bx*2.1, 3*by); |
|||
c3 = lerpColor(black, plum, s3/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c3); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), (7*by)-(2*by)*(mass[3]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[3]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s3 <= 63) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), 4*by, bx*2.1, 3*by); |
|||
c3 = lerpColor(plum, navy, (s3-32)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c3); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), (7*by)-(2*by)*(mass[3]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[3]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s3 <= 95) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), 4*by, bx*2.1, 3*by); |
|||
c3 = lerpColor(navy, sky, (s3-63)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c3); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), (7*by)-(2*by)*(mass[3]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[3]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s3 <= 127) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), 4*by, bx*2.1, 3*by); |
|||
c3 = lerpColor(sky, lime, (s3-95)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c3); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), (7*by)-(2*by)*(mass[3]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[3]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s3 <= 159) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), 4*by, bx*2.1, 3*by); |
|||
c3 = lerpColor(lime, sun, (s3-127)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c3); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), (7*by)-(2*by)*(mass[3]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[3]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s3 <= 191) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), 4*by, bx*2.1, 3*by); |
|||
c3 = lerpColor(sun, fire, (s3-159)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c3); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), (7*by)-(2*by)*(mass[3]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[3]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s3 <= 223) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), 4*by, bx*2.1, 3*by); |
|||
c3 = lerpColor(fire, tomato, (s3-191)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c3); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), (7*by)-(2*by)*(mass[3]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[3]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (s3 <= 255) { |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), 4*by, bx*2.1, 3*by); |
|||
c3 = lerpColor(tomato, orchid, (s3-223)/32); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
fill(c3); |
|||
rect((x+(bx*5)), (7*by)-(2*by)*(mass[3]/255), bx*2, (2*by)*(mass[3]/255)); |
|||
} |
|||
//displaying text for mass |
|||
/* |
|||
PFont font; |
|||
font = loadFont("Calibri-18.vlw"); |
|||
textFont(font, 18); |
|||
fill(0); |
|||
text(str0, x+bx, 3.1*by, 300, 30); |
|||
text(str1, x+(bx*5), 3.1*by, 300, 30); |
|||
text(str2, x+bx, 7.1*by, 300, 30); |
|||
text(str3, x+(bx*5), 7.1*by, 300, 30); |
|||
*/ |
|||
//displaying the mass amplitude values. We are also using a grayed-out rectangle to erase the previous text here |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect(x+bx, 3.5*by, bx*2.1, -12); |
|||
fill(0); |
|||
text(s0, x+bx, 3.5*by); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect(x+(bx*5), 3.5*by, bx*2.1, -12); |
|||
fill(0); |
|||
text(s1, x+(bx*5), 3.5*by); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect(x+bx, 7.5*by, bx*2.1, -12); |
|||
fill(0); |
|||
text(s2, x+bx, 7.5*by); |
|||
fill(102); |
|||
rect(x+(bx*5), 7.5*by, bx*2.1, -12); |
|||
fill(0); |
|||
text(s3, x+(bx*5), 7.5*by); |
|||
</pre> |
|||
Creating color references next to the colorbars (found within colorbars();) |
|||
<pre> |
|||
//color references, these are guides next to the colorbars to show what colors to expect at certain |
|||
//mass amplitudes. These references are 5 pixels wide and 88 pixels long and similarly have 8 intervals |
|||
//for color interpolation. |
|||
for (float i=0; i<=87; i++) { |
|||
if (i <= 10) { |
|||
r0 = lerpColor(black, plum, i/11); |
|||
stroke(r0); |
|||
line((3*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*3)-i, (3*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*3)-i); |
|||
line((7*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*3)-i, (7*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*3)-i); |
|||
line((3*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*7)-i, (3*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*7)-i); |
|||
line((7*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*7)-i, (7*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*7)-i); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (i <= 21) { |
|||
r0 = lerpColor(plum, navy, (i-10)/11); |
|||
stroke(r0); |
|||
line((3*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*3)-i, (3*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*3)-i); |
|||
line((7*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*3)-i, (7*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*3)-i); |
|||
line((3*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*7)-i, (3*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*7)-i); |
|||
line((7*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*7)-i, (7*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*7)-i); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (i <= 32) { |
|||
r0 = lerpColor(navy, sky, (i-21)/11); |
|||
stroke(r0); |
|||
line((3*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*3)-i, (3*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*3)-i); |
|||
line((7*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*3)-i, (7*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*3)-i); |
|||
line((3*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*7)-i, (3*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*7)-i); |
|||
line((7*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*7)-i, (7*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*7)-i); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (i <= 43) { |
|||
r0 = lerpColor(sky, lime, (i-32)/11); |
|||
stroke(r0); |
|||
line((3*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*3)-i, (3*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*3)-i); |
|||
line((7*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*3)-i, (7*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*3)-i); |
|||
line((3*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*7)-i, (3*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*7)-i); |
|||
line((7*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*7)-i, (7*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*7)-i); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (i <= 54) { |
|||
r0 = lerpColor(lime, sun, (i-43)/11); |
|||
stroke(r0); |
|||
line((3*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*3)-i, (3*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*3)-i); |
|||
line((7*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*3)-i, (7*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*3)-i); |
|||
line((3*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*7)-i, (3*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*7)-i); |
|||
line((7*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*7)-i, (7*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*7)-i); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (i <= 65) { |
|||
r0 = lerpColor(sun, fire, (i-54)/11); |
|||
stroke(r0); |
|||
line((3*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*3)-i, (3*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*3)-i); |
|||
line((7*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*3)-i, (7*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*3)-i); |
|||
line((3*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*7)-i, (3*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*7)-i); |
|||
line((7*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*7)-i, (7*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*7)-i); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (i <= 76) { |
|||
r0 = lerpColor(fire, tomato, (i-65)/11); |
|||
stroke(r0); |
|||
line((3*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*3)-i, (3*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*3)-i); |
|||
line((7*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*3)-i, (7*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*3)-i); |
|||
line((3*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*7)-i, (3*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*7)-i); |
|||
line((7*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*7)-i, (7*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*7)-i); |
|||
} |
|||
else if (i <= 87) { |
|||
r0 = lerpColor(tomato, orchid, (i-76)/11); |
|||
stroke(r0); |
|||
line((3*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*3)-i, (3*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*3)-i); |
|||
line((7*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*3)-i, (7*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*3)-i); |
|||
line((3*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*7)-i, (3*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*7)-i); |
|||
line((7*bx+10+window_width/2), (by*7)-i, (7*bx)+15+window_width/2, (by*7)-i); |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
//creating an outline around the color references |
|||
noFill(); |
|||
stroke(0); |
|||
rect((3*bx+9+window_width/2), (by*3), 7, -88); |
|||
rect((7*bx+9+window_width/2), (by*3), 7, -88); |
|||
rect((3*bx+9+window_width/2), (by*7), 7, -88); |
|||
rect((7*bx+9+window_width/2), (by*7), 7, -88); |
|||
</pre> |
|||
X-position vs. time and Y-position vs. time plots section found inside colorbars(); |
|||
<pre> |
|||
/*x-position vs time plot |
|||
we use the same calculations as in the xposition(); and yposition();. We are |
|||
also using the "erasing rectangle" algorithm in plotting points. The speed of dot-plotting (according to the |
|||
x-position) is the speed the computer can run through draw(); because a dot is plotted each time the code for |
|||
this section is processed. After a dot is plotted, a rectangle including that dot is copied and moved to the |
|||
right 1 dot-width to the right. The original dot is erased with a erasing rectangle 1 dot-width long. Then, |
|||
the next dot is plotted where the last dot was originally plotted (at the very left of the window) when this |
|||
section of code is run through again. |
|||
*/ |
|||
stroke(max(c0,c2)); |
|||
float L; |
|||
float R; |
|||
float Xpos; |
|||
L = (mass[0]+mass[2])/2; |
|||
R = (mass[1]+mass[3])/2; |
|||
Xpos = R-L; |
|||
strokeWeight(4); |
|||
point(29,(Xpos/1.52)+window_height/2); |
|||
strokeWeight(1); |
|||
copy(27, int(window_height/3)+30, int(window_width/2)-54, int(window_height/3)-60, 30, int(window_height/3)+30, int(window_width/2)-54, int(window_height/3)-60); |
|||
fill(255); |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
rect(26, int(window_height/3)+30, 4, int(window_height/3)-60); |
|||
//y-position vs time plot |
|||
stroke(max(c0,c1)); |
|||
float T; |
|||
float B; |
|||
float Ypos; |
|||
T = (mass[0]+mass[1])/2; |
|||
B = (mass[2]+mass[3])/2; |
|||
Ypos = B-T; |
|||
strokeWeight(4); |
|||
point(29,(Ypos/1.52)+window_height*0.8333); |
|||
strokeWeight(1); |
|||
copy(27, int(window_height*2/3)+30, int(window_width/2)-54, int(window_height/3)-60, 30, int(window_height*2/3)+30, int(window_width/2)-54, int(window_height/3)-60); |
|||
fill(255); |
|||
noStroke(); |
|||
rect(26, int(window_height*2/3)+30, 4, int(window_height/3)-60); |
|||
//midline for x-position vs. time, and y-position vs. time plots |
|||
stroke(75); |
|||
line(26, int(window_height*0.8333), int(window_width/2)-25, int(window_height*0.8333)); |
|||
line(26, int(window_height/2), int(window_width/2)-25, int(window_height/2)); |
|||
} |
|||
</pre> |
|||
Latest revision as of 15:21, 1 March 2010
Overview
A BME Senior Design project group is developing a device to measure the weight shifting ability of a child with Cerebral Palsy. The end goal is to develop a video game that is controlled by the child shifting their weight. Hopefully this device will allow the children to improve their balance while having fun playing a video game.
Our portion of the project involves designing the hardware to read the signals from 4 load cells and writing code to read in the load values to a PIC 32 microcontroller which is then sent to a PC via RS232. Additionally we developed an interface for the PC that visually represents the collected data in a useful and intuitive format.
Circuit
Each load sensor acts as a half bridge rectifier. When a potential difference is applied across the bridge, changes in load can be measured by sensing the voltage change at the middle of the bridge. This voltage change will be on the order of a few microvolts for most load cells.
In order to read this very small change in voltage you need to use an [Instrumentation Amplifier]. Instrumentation amplifiers read in two voltages and multiply the difference by a value specified by an external gain resistor.
To complete the second half of the Wheatstone bridge a potentiometer is used. This potentiometer can be tuned to match the voltage produced by the load cell when no weight is applied. Therefore as more weight is applied the voltage out of the amplifier will increase until saturation of the amp is reached. This tunning is very important and can be time consuming because an initial offset of a few millivolts can force the amplifier to saturation.
The signal that leaves the amp is fairly noisy so a low pass filter is used to smooth out the signal that is sent to the ADC.
PIC Code
The purpose of this code is to take the input signals (amplified voltage differences) from the 4 individual force sensors on the scale and output a string of 4 floats separated by spaces ending with a new line. This string will be sent out using RS232 and deciphered by Processing.
ADC: In order to use the Analog-to-Digital converter embedded in PIC, we used Nick’s example, PIC32MX: Analog Input. Copy all the lines in this link except for the infinite while loop. However, you want to have four analog inputs for this project therefore you will need to change the number of analog inputs since this example only uses two analog inputs. Do the following modifications in order to have four analog inputs.
- define PARAM2, you need four samples, so change ADC_SAMPLES_PER_INT_2 --> ADC_SAMPLES_PER_INT_4.
- define PARAM4, you also need to enable AN3 and AN4 as well with AN1 and AN2,
- define PARAM5, you don’t want to skip AN3 and AN4, so remove these two inputs from this parameter.
Interrupt Handler: This function will affect our code only if the PIC receives a data from the processing via RS232 cable. If the interrupt occurs, it will first check whether the receive input interrupt flag was generated or transmit output interrupt flag was generated. And if it was the receive input interrupt, then it will save the value it received to the volatile unsigned char data, which we declared as a global variable. Then, the next line of code is a switch statement. If it reads the character 'p' from volatile unsigned char data, which is sent from Processing when the 'zero out sensors' button is pressed, then it will record the initial values of the four sensors.
The full code can be found here.
"main.c"
Main Function
int main(void)
{
int pbClk;
// Sets the B port to Analog Input
AD1PCFG = 0xFFFF;
// Configure the proper PB frequency and the number of wait states
pbClk = SYSTEMConfigPerformance(SYS_FREQ);
// Allow vector interrupts
INTEnableSystemMultiVectoredInt();
mInitAllLEDs();
initUART2(pbClk);
initADC();
while(1)
{
// read each sensor, subtract zero state value,
top_left= ReadADC10(0)-top_left_initial;
top_right= ReadADC10(1)-top_right_initial;
bottom_left= ReadADC10(2)-bottom_left_initial;
bottom_right= ReadADC10(3)-bottom_right_initial;
//Send to PC via RS232
sendDataRS232();
}
} //end main
Processing Code
The Processing portion of our lab involves 4 visible sections:
1. Colorbars, colorbars();
continuously displaying the force applied onto each force sensor by using 4 bars that will grow or shrink depending on the amplitude of mass (force). The bars will also show the amplitude of the mass by changing colors. When 0 or little force is applied, then corresponding bar is black colored, at the max force, the bar is orchid (pink) colored.
2. XY-Plot, xyplot();
continuously displays the x- and y- position of the center of balance calculated between all 4 sensors with a dot on a xy-coordinate plane. So, if the person shifts his weight to the right side of scale, then the dot will move to the right in the x direction. If the person shifts his weight to the front of the sensor, then the dot will move up in the y direction. The corners represent one sensor at it's maximum amplitude (of 255) with the rest of the sensors at zero amplitude.
3. X-position vs. Time (not a separate function)
continuously plots a dot for the x-position along a time axis. This plot will be useful to see how much the person shifts his/her weight to the left or right (lateral shift) over time. Due to the window size and the speed of processing, the points will be plotted over a time period of about 20 seconds.
4. Y-position vs. time (not a separate function)
continuously plots a dot for the y-position along a time axis. This plot will be useful to see how much the person shifts his/her weight forward or backwards (anteroposterior shift) over time. The code for this section is essentially the same as the x-position but edited to show y-position.
Screenshots: exerting force on the sensors in a circular pattern (left) and exerting force on one sensor at a time (right).
Other Important Functions:
1. Communication between the PC (Processing) and the PIC via RS232, void initSerial();
The purpose of InitSerial(); is to open a serial port on the PC and communicate with the PIC32. The code found here is essentially a modification of the ME333 Lab 4: Motor Control Processing code written by Nick Marchuk.
2. X-position, float xposition();
Calculates the x-position based on the contribution of each force sensor output and returns the resulting float value.
3. Y-position, float yposition();
Calculates the y-position based on the contribution of each force sensor output and returns the resulting float value.
4. Button to zero out force sensors
Adds a button to zero out the force sensors. Noise displaces our dot in the xy-plot from the center when we first turn on our circuit. There is an interrupt function in the main.c file that will do the "zeroing out" and output altered values once this button is pressed. The code for this button was taken from ME333 Lab 4: Motor Control, written by Nick Marchuk.
Notes on relative amplitude range and mapping:
Our code was written with the assumption that the inputs from the PIC (that initially comes from the 4 force sensors) will come in the form of a 4x1 array. It does not actually arrive in that form from the PIC, it actually arrives as a string of floats separated by spaces ending with a new line. The new line is deleted and the floats are extracted out, normalized between 0-255, and put into the "mass" array. All of the normalization, window dimension parameters, rectangle dimensions, etc. were set up with the 0-255 range and 1000x700 window size in mind. So if the values are not between 0-255 or the window size is altered, almost all of following code will be messed up. The x-position vs. time and y-position vs. time plots are not implemented as independent functions. The code for these plots are found at the very end of colorbars();.
One of the global variables, mapping integer "m," determines the sensitivity of the sensors. Our potentiometers are tuned to output a miniscule positive voltage difference which is amplified by 675. The resulting value falls within our initial range of 0-m (default: 0-511) which is then mapped to a floating-point number range 0-255. We found that the default initial range of 0-511 (m = 511) works well for adults standing on the scale. For adults using their hands to exert force on the scale, the range 0-200 (m = 200) is more suitable. Thus, as m is decreased, the sensitivity is increased. This mapping variable can be altered for each individual user, especially cerebral palsy patients, for which this scale is designed.
Next Steps
1. Develop a printed circuit board that contains all amplification circuitry, the microcontroller, and tunning circuits. Additionally, redesign the tunning circuit so that it is more robust.
2. Find a formula(hopefully linear) that equates the voltages seen from the sensors to mass. This can be done by using a few objects whose mass's are known.
3. Develop a chart that details what the "m" mapping variable value should be for a user's body weight and configure the scale to automatically adjust the m value when a user steps on the scale.
4. Also, make the colorbars or plot dots change to a certain color and/or have the computer play a sound when a certain mass amplitude value on a sensor has been breached. This may be useful for cerebral palsy patients that are being trained to maintain balance.
Files
The full Processing code can be found here.
A full zip file containing the PIC code, Processing code, images, screenshots can be found here.
A link to a demonstration video of the force sensing scale can be found here.