Difference between revisions of "PIC/C18 Compiler Tips and Troubleshooting"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__TOC__ |
__TOC__ |
||
==Troubleshooting== |
==Troubleshooting== |
||
=== |
===MPLAB Has Trouble Connecting to the ICD2=== |
||
If you see the following errors while trying to connect to the ICD2: |
If you see the following errors while trying to connect to the ICD2: |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
</pre> |
</pre> |
||
Disconnect the reconnect the ICD2 from the USB port, then open the Device Manager ('''Control panel>System>Hardware>Device Manager''') and disable then re-enable the ICD2. Also, be sure that you followed in installation instructions in the manual when you installed the ICD2. |
Disconnect the reconnect the ICD2 from the USB port, then open the Device Manager ('''Control panel>System>Hardware>Device Manager''') and disable then re-enable the ICD2. Also, be sure that you followed in installation instructions in the manual when you installed the ICD2. |
||
===printf=== |
===printf=== |
||
Revision as of 20:15, 29 August 2007
Troubleshooting
MPLAB Has Trouble Connecting to the ICD2
If you see the following errors while trying to connect to the ICD2:
ICD0192: Failed to clear COM error. (RetVal = 0xFFFFFFF0, ErrRet = 0x0) ICD0021: Unable to connect with MPLAB ICD 2 ICD0019: Communications: Failed to open port: (Windows::GetLastError() = 0x2, 'The system cannot find the file specified. ') ICD0021: Unable to connect with MPLAB ICD 2
Disconnect the reconnect the ICD2 from the USB port, then open the Device Manager (Control panel>System>Hardware>Device Manager) and disable then re-enable the ICD2. Also, be sure that you followed in installation instructions in the manual when you installed the ICD2.
printf
Note that printing floating point types with printf is not supported.
Tips
Splitting Multi-Byte Data Types into Individual Bytes
There are some situations where you may need to split a multi-byte variable into its component bytes (for example, writing to 16-bit registers or sending data through the serial port).
Using Unions
One way to do this is to use the union data type. A union is like a struct, except all the members share the same location in memory. Therefore, if have a union with one int variable and an array of two char variables, writing to the int variable will automatically fill in the char as well, and vice versa.
Example:
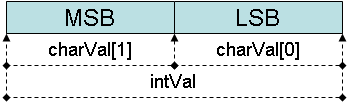
union UINT_UCHAR{
unsigned int intVal;
unsigned char charVal[2];
};
char byte1;
char byte2;
union UINT_UCHAR splitter;
splitter.intVal=0xABCD;
byte2=splitter.charVal[1]; //byte2 will equal 0xAB
byte1=splitter.charVal[0]; //byte1 will equal 0xCD
In the memory, it looks like this:
(MSB=Most Significant Byte, LSB=Least Significant Byte)
Using Arithmetic
Another way of doing this is to use arithmetic. For a 16-bit integer, the most significant byte can be obtained by dividing the value by 256. The least significant byte can be obtained by using the modulus function with 256. Example:
int someInteger; char byte1; char byte2; someInteger = 0xABCD; byte2 = someInteger/256; byte1 = someInteger%256;