Difference between revisions of "Guitar Tuning Project"
From Mech
Jump to navigationJump to search| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==Mechanical Design and machining== |
==Mechanical Design and machining== |
||
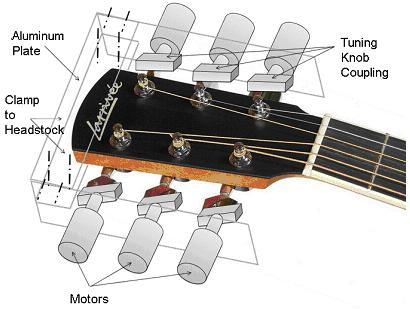
A head fit accustomed to the guitar is designed and machined. 6 DC motors are mounted on the outer surface of the side aluminum plate. |
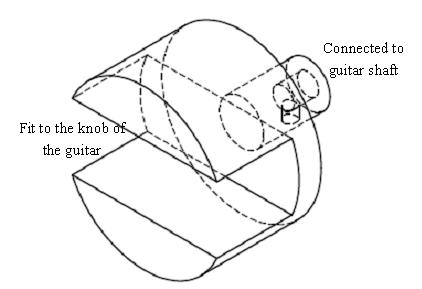
A head fit accustomed to the guitar is designed and machined. 6 DC motors are mounted on the outer surface of the side aluminum plate. 6 knob couplings are machined. The knob coupling is shown as following. The slot is to fit the knobs of the guitar while the hole in the other is to fit into the shaft of the DC motor. There is a set screw hole letting a set screw to hold the shaft tight to the hole. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
6 knob couplings are machined. The knob coupling is shown as following. The slot is to fit the knobs of the guitar while the hole in the other is to fit into the shaft of the DC motor. There is a set screw hole letting a set screw to hold the shaft tight to the hole. |
|||
Revision as of 18:18, 6 December 2008
Guitar Tuning Project (GTTP)
Overview
Project Goal --- Achieve guitar tuning function. By manually plucking a guitar string, the system will determine whether the frequency is higher or lower than the set frequency. Based on the results, the system will tune the string's vibration frequency to the set frequency with a small error range (0.5Hz?).
System Diagram
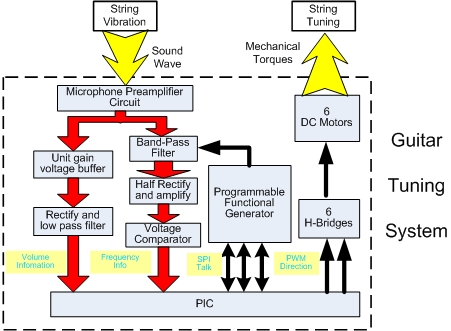
The whole system is shown in following figure. The microphone and preamplifier convert the sound wave into a voltage wave and amplify it into AC voltage signal. This AC voltage signal goes into 2 directions. The 1st direction goes into a unit gain voltage buffer and then converted into a DC signal after rectifying and low-pass filtering. This DC signal provides the volume information of the sound wave to the PIC. The 2nd direction goes into a Band-Pass filter. Because the AC voltage signal from the preamplifier contains a lot of environmental noise as well as harmonic waves. The band-pass filter can let a narrow band pass. The band-pass properties are controlled by the centering frequency set by a programmable waveform generator communicating with PIC. After the band-pass filter, the signal is a fairly clean sine wave signal. This signal experiences half-wave rectifying and amplifying. Later it goes into the voltage comparator and becomes a square wave. This square wave is connected to the I/O pin of the PIC and the sound frequency is calculated by the PIC based upon this signal. With the calculated frequency of the current sound wave of the string, PIC compares it to the accurate frequency of the string stored in the program and generates corresponding control signals to control 6 DC motors using H bridges to tune the guitar string till the string's frequency approximates the standard frequency by a limited error (0.5Hz?)
Circuit Design and building
Microphone and preamplifier circuit
Unit Gain Voltage buffer
Rectify and low pass filter
Voltage Comparator
Programmable Function generator (Using AD9833)
Band-pass filter (Using LMF100)
Software coding
algorithm
Mechanical Design and machining
A head fit accustomed to the guitar is designed and machined. 6 DC motors are mounted on the outer surface of the side aluminum plate. 6 knob couplings are machined. The knob coupling is shown as following. The slot is to fit the knobs of the guitar while the hole in the other is to fit into the shaft of the DC motor. There is a set screw hole letting a set screw to hold the shaft tight to the hole.