Difference between revisions of "Gears"
From Mech
Jump to navigationJump to searchm (→Gear Forces) |
m (→Types of Gears) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Types of Gears== |
==Types of Gears== |
||
{| |
|||
! width="150px" | Spur Gears |
|||
! width="150px" | Rack and Pinion |
|||
! width="150px" | Bevel Gears |
|||
! width="150px" | Helical Gears |
|||
! width="150px" | Worm Drives |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[image:spur gears.png|125px|center]] |
|||
| [[image:rack and pinion.png|125px|center]] |
|||
| [[image:bevel gears.png|125px|center]] |
|||
| [[image:helical gears.png|125px|center]] |
|||
| [[image:worm drive.png|125px|center]] |
|||
|} |
|||
==Gear Geometry== |
==Gear Geometry== |
||
Revision as of 16:11, 4 July 2006
Types of Gears
| Spur Gears | Rack and Pinion | Bevel Gears | Helical Gears | Worm Drives |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Gear Geometry
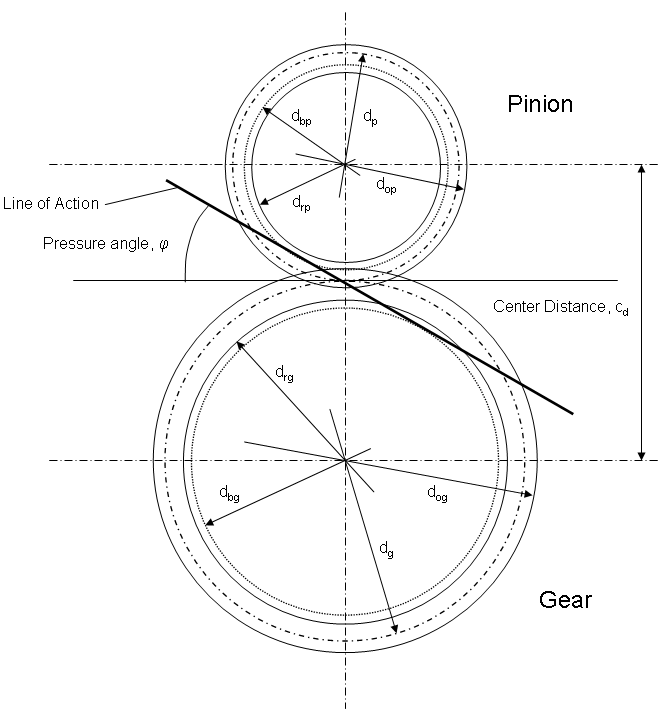
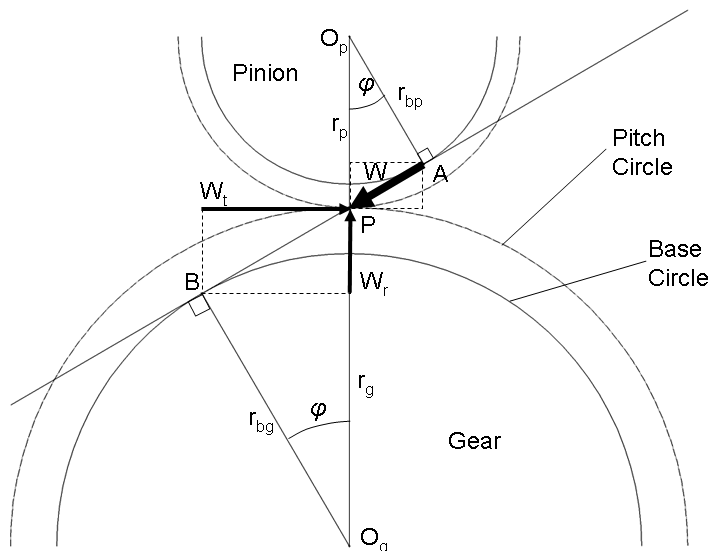
For external spur gears (most common), the gear geometry is as shown in the figure below. The line of action is the line that passes through the intersection of the pitch circles and also tangent to the base circles.
Gear Meshing
Gear Forces
Gear meshing results in contacts with normals along the line of action, so the resultant force, is along this line. This results in both tangential and radial forces, and , on the gear pair. When these gears are mounted on a shaft, the radial force causes a bending moment while the tangent force causes both a bending moment and a torque.